Terahertz endoscopic imaging for colorectal cancer detection: Current status and future perspectives
- PMID: 28874955
- PMCID: PMC5565500
- DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i8.346
Terahertz endoscopic imaging for colorectal cancer detection: Current status and future perspectives
Abstract
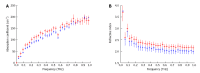
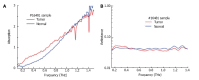
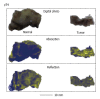
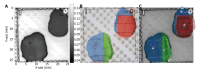
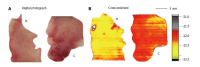
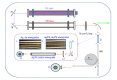
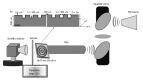
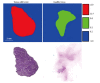
Terahertz (THz) imaging is progressing as a robust platform for myriad applications in the field of security, health, and material science. The THz regime, which comprises wavelengths spanning from microns to millimeters, is non-ionizing and has very low photon energy: Making it inherently safe for biological imaging. Colorectal cancer is one of the most common causes of death in the world, while the conventional screening and standard of care yet relies exclusively on the physician's experience. Researchers have been working on the development of a flexible THz endoscope, as a potential tool to aid in colorectal cancer screening. This involves building a single-channel THz endoscope, and profiling the THz response from colorectal tissue, and demonstrating endogenous contrast levels between normal and diseased tissue when imaging in reflection modality. The current level of contrast provided by the prototype THz endoscopic system represents a significant step towards clinical endoscopic application of THz technology for in-vivo colorectal cancer screening. The aim of this paper is to provide a short review of the recent advances in THz endoscopic technology and cancer imaging. In particular, the potential of single-channel THz endoscopic imaging for colonic cancer screening will be highlighted.
Keywords: Cancer detection; Colon; Colonoscopy; Cross-pol; Endoscopy; Flexible waveguides; Metal-coated; Polarization; Polarization-sensitive; Terahertz imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Authors declare no conflicts of interests for this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging: A Cutting-Edge Method for Diagnosing Digestive Cancers.Materials (Basel). 2019 May 9;12(9):1519. doi: 10.3390/ma12091519. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31075912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-channel prototype terahertz endoscopic system.J Biomed Opt. 2014 Aug;19(8):080501. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.19.8.080501. J Biomed Opt. 2014. PMID: 25111144
-
Advances in terahertz technology for cancer detection applications.Opt Quantum Electron. 2023;55(2):151. doi: 10.1007/s11082-022-04340-0. Epub 2022 Dec 26. Opt Quantum Electron. 2023. PMID: 36588663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomedical application of terahertz imaging technology: a narrative review.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Dec 1;13(12):8768-8786. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-526. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 38106329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoscale biomaterials for terahertz imaging: A non-invasive approach for early cancer detection.Transl Oncol. 2023 Jan;27:101565. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101565. Epub 2022 Nov 4. Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36343417 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging: A Cutting-Edge Method for Diagnosing Digestive Cancers.Materials (Basel). 2019 May 9;12(9):1519. doi: 10.3390/ma12091519. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31075912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy for non-invasive assessment of water content in biological samples.Biomed Opt Express. 2018 Apr 20;9(5):2266-2276. doi: 10.1364/BOE.9.002266. eCollection 2018 May 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2018. PMID: 29760985 Free PMC article.
-
Polarimetry terahertz imaging of human breast cancer surgical specimens.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2024 Nov;11(6):065503. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.11.6.065503. Epub 2024 Dec 5. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2024. PMID: 39649775
-
The medical application of terahertz technology in non-invasive detection of cells and tissues: opportunities and challenges.RSC Adv. 2019 Mar 22;9(17):9354-9363. doi: 10.1039/c8ra10605c. eCollection 2019 Mar 22. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35520739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct and integrating sampling in terahertz receivers from wafer-scalable InAs nanowires.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 2;15(1):103. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44345-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38167839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Bond JH, Ahnen DJ, Garewal H, Chejfec G. Use of colonoscopy to screen asymptomatic adults for colorectal cancer. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group 380. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:162–168. - PubMed
-
- Müller AD, Sonnenberg A. Prevention of colorectal cancer by flexible endoscopy and polypectomy. A case-control study of 32,702 veterans. Ann Intern Med. 1995;123:904–910. - PubMed
-
- Hariri LP, Tumlinson AR, Besselsen DG, Utzinger U, Gerner EW, Barton JK. Endoscopic optical coherence tomography and laser induced fluorescence spectroscopy in a murine colon cancer model. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine. 2006;38:305–313. - PubMed
-
- Fercher AF, Drexler W, Hitzenberger CK, Lasser T. Optical coherence tomography-principles and applications. Reports on Progress in Physics. 2003;66:239.
-
- Veerappan GR, Ally MR, Choi JH, Pak JS, Maydonovitch C, Wong RK. Extracolonic findings on CT colonography increases yield of colorectal cancer screening. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;195:677–686. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

