Inhibition of Angiogenesis: A Novel Effect of Zataria Multiflora
- PMID: 28875003
- PMCID: PMC5575732
Inhibition of Angiogenesis: A Novel Effect of Zataria Multiflora
Abstract
Background: Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels from preexisting ones, is among the most important physiological and pathological processes that occur in the body. Under pathological conditions such as tumor growth, psoriasis, corneal neovascularization and rheumatoid arthritis, angiogenesis is substantial for the development of the disease. Zataria multiflora is a member of the Labiatae family with a vast range of traditional uses which has been long known and applied in Iran old medicine. The aim of this study was the evaluation of anti-angiogenic potential of Zataria multiflora. Materials and Methods: In this study, human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were isolated from newborn umbilical veins and then cultured for cytotoxicity (LDH test) assay. Regarding LDH results, following tests such as angiogenesis (cytodex-3 micro carrier) and migration (wound healing) tests were designed. Results: The cytotoxicity assays showed no toxicity of Z.multiflora toward HUVECs in the range of 10-450µg/mL of the extract. This extract was also able to inhibit angiogenesis and migration at 200µg/mL. Conclusion: Our data clearly demonstrated an inhibitory effect of Z. multiflora on angiogenesis and migration of HUVECs. Z. multiflora could be introduced as a significant angiogenesis inhibitor for angiogenesis-dependent diseases in further complementary studies.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Cell migration; Endothelial cells; Zataria multiflora.
Figures
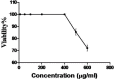

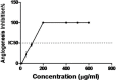



References
-
- Mostafaie A, Mohammadi-Motlagh HR, Mansouri K. Angiogenesis and the models to study angiogenesis. Yakhteh Med J. 2010;11:374–381.
-
- Norooznezhad AH, Norooznezhad F. How Could Cannabinoids Be Effective in Multiple Evanescent White Dot Syndrome? A Hypothesis. J Rep Pharm Sci. 2016;5:49–52.
-
- Shakiba Y, Mansouri K, Arshadi D, et al. Corneal neovascularization: molecular events and therapeutic options. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2009;3(3):221–231. - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich R, Röcken M, Ghoreschi K. Angiogenesis: the new potential target for treatment of psoriasis? Drug News Perspect. 2008;21(2):97–105. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
