Ceftazidime-avibactam has potent sterilizing activity against highly drug-resistant tuberculosis
- PMID: 28875168
- PMCID: PMC5576880
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1701102
Ceftazidime-avibactam has potent sterilizing activity against highly drug-resistant tuberculosis
Abstract
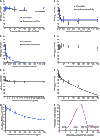
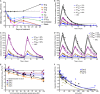
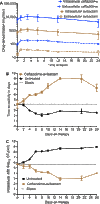
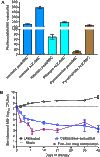
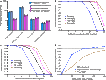
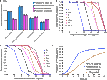
There are currently many patients with multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Ongoing transmission of the highly drug-resistant strains and high mortality despite treatment remain problematic. The current strategy of drug discovery and development takes up to a decade to bring a new drug to clinical use. We embarked on a strategy to screen all antibiotics in current use and examined them for use in tuberculosis. We found that ceftazidime-avibactam, which is already used in the clinic for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacillary infections, markedly killed rapidly growing, intracellular, and semidormant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the hollow fiber system model. Moreover, multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant clinical isolates demonstrated good ceftazidime-avibactam susceptibility profiles and were inhibited by clinically achievable concentrations. Resistance arose because of mutations in the transpeptidase domain of the penicillin-binding protein PonA1, suggesting that the drug kills M. tuberculosis bacilli via interference with cell wall remodeling. We identified concentrations (exposure targets) for optimal effect in tuberculosis, which we used with susceptibility results in computer-aided clinical trial simulations to identify doses for immediate clinical use as salvage therapy for adults and young children. Moreover, this work provides a roadmap for efficient and timely evaluation of antibiotics and optimization of clinically relevant dosing regimens.
Figures

References
-
- Dheda K., Gumbo T., Maartens G., Dooley K. E., McNerney R., Murray M., Furin J., Nardell E. A., London L., Lessem E., Theron G., van Helden P., Niemann S., Merker M., Dowdy D., Van Rie A., Siu G. K., Pasipanodya J. G., Rodrigues C., Clark T. G., Sirgel F. A., Esmail A., Lin H. H., Atre S. R., Schaaf H. S., Chang K. C., Lange C., Nahid P., Udwadia Z. F., Horsburgh C. R. Jr., Churchyard G. J., Menzies D., Hesseling A. C., Nuermberger E., McIlleron H., Fennelly K. P., Goemaere E., Jaramillo E., Low M., Jara C. M., Padayatchi N., Warren R. M., The epidemiology, pathogenesis, transmission, diagnosis, and management of multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant, and incurable tuberculosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 5, 291–360 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Dheda K., Limberis J. D., Pietersen E., Phelan J., Esmail A., Lesosky M., Fennelly K. P., te Riele J., Mastrapa B., Streicher E. M., Dolby T., Abdallah A. M., Ben-Rached F., Simpson J., Smith L., Gumbo T., van Helden P., Sirgel F. A., McNerney R., Theron G., Pain A., Clark T. G., Warren R. M., Outcomes, infectiousness, and transmission dynamics of patients with extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis and home-discharged patients with programmatically incurable tuberculosis: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 5, 269–281 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Bloemberg G. V., Keller P. M., Stucki D., Trauner A., Borrell S., Latshang T., Coscolla M., Rothe T., Homke R., Ritter C., Feldmann J., Schulthess B., Gagneux S., Böttger E. C., Acquired resistance to bedaquiline and delamanid in therapy for tuberculosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 373, 1986–1988 (2015). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pym A. S., Diacon A. H., Tang S. J., Conradie F., Danilovits M., Chuchottaworn C., Vasilyeva I., Andries K., Bakare N., De Marez T., Haxaire-Theeuwes M., Lounis N., Meyvisch P., Van Baelen B., van Heeswijk R. P., Dannemann B.; TMC207-C209 Study Group, Bedaquiline in the treatment of multidrug- and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Eur. Respir. J. 47, 564–574 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

