Interplay Between n-3 and n-6 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Endocannabinoid System in Brain Protection and Repair
- PMID: 28875399
- PMCID: PMC5656721
- DOI: 10.1007/s11745-017-4292-8
Interplay Between n-3 and n-6 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Endocannabinoid System in Brain Protection and Repair
Abstract
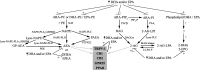
The brain is enriched in arachidonic acid (ARA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFAs) of the n-6 and n-3 series, respectively. Both are essential for optimal brain development and function. Dietary enrichment with DHA and other long-chain n-3 PUFA, such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), has shown beneficial effects on learning and memory, neuroinflammatory processes, and synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis. ARA, DHA and EPA are precursors to a diverse repertoire of bioactive lipid mediators, including endocannabinoids. The endocannabinoid system comprises cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, the endocannabinoids, and their biosynthetic and degradation enzymes. Anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) are the most widely studied endocannabinoids and are both derived from phospholipid-bound ARA. The endocannabinoid system also has well-established roles in neuroinflammation, synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis, suggesting an overlap in the neuroprotective effects observed with these different classes of lipids. Indeed, growing evidence suggests a complex interplay between n-3 and n-6 LCPUFA and the endocannabinoid system. For example, long-term DHA and EPA supplementation reduces AEA and 2-AG levels, with reciprocal increases in levels of the analogous endocannabinoid-like DHA and EPA-derived molecules. This review summarises current evidence of this interplay and discusses the therapeutic potential for brain protection and repair.
Keywords: Endocannabinoid system; Neurogenesis; Neuroinflammation; Omega-3 fatty acids; Omega-6 fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Micha R, Khatibzadeh S, Shi P, Fahimi S, Lim S, Andrews KG, Engell RE, Powles J, Ezzati M, Mozaffarian D. Global, regional, and national consumption levels of dietary fats and oils in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis including 266 country-specific nutrition surveys. BMJ. 2014;348:g2272. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g2272. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

