Incidence, Predictors, and Clinical Outcomes of New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention with Drug-Eluting Stent
- PMID: 28875603
- PMCID: PMC5592173
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.10.1603
Incidence, Predictors, and Clinical Outcomes of New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention with Drug-Eluting Stent
Abstract
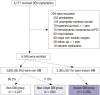
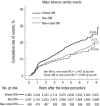
We investigated the incidence, predictors, and long-term clinical outcomes of new-onset diabetes mellitus (DM) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with drug-eluting stent (DES). A total of 6,048 patients treated with DES were retrospectively reviewed and divided into three groups: 1) known DM (n = 2,365; fasting glucose > 126 mg/dL, glycated hemoglobin > 6.5%, already receiving DM treatment, or previous history of DM at the time of PCI); 2) non-DM (n = 3,247; no history of DM, no laboratory findings suggestive of DM at PCI, and no occurrence of DM during follow-up); and 3) new-onset DM (n = 436; non-DM features at PCI and occurrence of DM during follow-up). Among 3,683 non-DM patients, 436 (11.8%) patients were diagnosed with new-onset DM at 3.4 ± 1.9 years after PCI. Independent predictors for new-onset DM were high-intensity statin therapy, high body mass index (BMI), and high level of fasting glucose and triglycerides. The 8-year cumulative rate of major adverse cardiac events (a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stent thrombosis, or any revascularization) in the new-onset DM group was 19.5%, which was similar to 20.5% in the non-DM group (P = 0.467), but lower than 25.0% in the known DM group (P = 0.003). In conclusion, the incidence of new-onset DM after PCI with DES was not low. High-intensity statin therapy, high BMI, and high level of fasting glucose and triglycerides were independent predictors for new-onset DM. Long-term clinical outcomes of patients with new-onset DM after PCI were similar to those of patients without DM.
Keywords: Coronary Artery Disease; Diabetes Mellitus; Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.
© 2017 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Hammoud T, Tanguay JF, Bourassa MG. Management of coronary artery disease: therapeutic options in patients with diabetes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36:355–365. - PubMed
-
- Grundy SM, Benjamin IJ, Burke GL, Chait A, Eckel RH, Howard BV, Mitch W, Smith SC, Jr, Sowers JR. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 1999;100:1134–1146. - PubMed
-
- Folsom AR, Szklo M, Stevens J, Liao F, Smith R, Eckfeldt JH. A prospective study of coronary heart disease in relation to fasting insulin, glucose, and diabetes. The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:935–942. - PubMed
-
- Becker A, Bos G, de Vegt F, Kostense PJ, Dekker JM, Nijpels G, Heine RJ, Bouter LM, Stehouwer CD. Cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes: comparison with nondiabetic individuals without and with prior cardiovascular disease. 10-year follow-up of the Hoorn Study. Eur Heart J. 2003;24:1406–1413. - PubMed
-
- Stone GW, Witzenbichler B, Weisz G, Rinaldi MJ, Neumann FJ, Metzger DC, Henry TD, Cox DA, Duffy PL, Mazzaferri E, et al. Platelet reactivity and clinical outcomes after coronary artery implantation of drug-eluting stents (ADAPT-DES): a prospective multicentre registry study. Lancet. 2013;382:614–623. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

