Genetic Associations with Gestational Duration and Spontaneous Preterm Birth
- PMID: 28877031
- PMCID: PMC5561422
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1612665
Genetic Associations with Gestational Duration and Spontaneous Preterm Birth
Abstract
Background: Despite evidence that genetic factors contribute to the duration of gestation and the risk of preterm birth, robust associations with genetic variants have not been identified. We used large data sets that included the gestational duration to determine possible genetic associations.
Methods: We performed a genomewide association study in a discovery set of samples obtained from 43,568 women of European ancestry using gestational duration as a continuous trait and term or preterm (<37 weeks) birth as a dichotomous outcome. We used samples from three Nordic data sets (involving a total of 8643 women) to test for replication of genomic loci that had significant genomewide association (P<5.0×10-8) or an association with suggestive significance (P<1.0×10-6) in the discovery set.
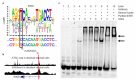
Results: In the discovery and replication data sets, four loci (EBF1, EEFSEC, AGTR2, and WNT4) were significantly associated with gestational duration. Functional analysis showed that an implicated variant in WNT4 alters the binding of the estrogen receptor. The association between variants in ADCY5 and RAP2C and gestational duration had suggestive significance in the discovery set and significant evidence of association in the replication sets; these variants also showed genomewide significance in a joint analysis. Common variants in EBF1, EEFSEC, and AGTR2 showed association with preterm birth with genomewide significance. An analysis of mother-infant dyads suggested that these variants act at the level of the maternal genome.
Conclusions: In this genomewide association study, we found that variants at the EBF1, EEFSEC, AGTR2, WNT4, ADCY5, and RAP2C loci were associated with gestational duration and variants at the EBF1, EEFSEC, and AGTR2 loci with preterm birth. Previously established roles of these genes in uterine development, maternal nutrition, and vascular control support their mechanistic involvement. (Funded by the March of Dimes and others.).
Figures


Comment in
-
Genetic Associations with Spontaneous Preterm Birth.N Engl J Med. 2017 Dec 14;377(24):2401. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1713902. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 29239589 No abstract available.
References
-
- Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Osterman MJ. Births in the United States, 2014. NCHS data brief 2015:1-8. - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Oza S, Hogan D, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000-13, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: an updated systematic analysis. Lancet 2015;385:430-40. - PubMed
-
- Butler AS, Behrman RE. Preterm Birth:: Causes, Consequences, and Prevention: National Academies Press; 2007. - PubMed
-
- Muglia LJ, Katz M. The enigma of spontaneous preterm birth. N Engl J Med 2010;362:529-35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
