Heparin Increases Food Intake through AgRP Neurons
- PMID: 28877477
- PMCID: PMC6310124
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.08.049
Heparin Increases Food Intake through AgRP Neurons
Abstract
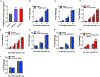
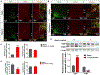
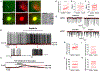
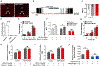
Although the widely used anticoagulant drug heparin has been shown to have many other biological functions independent of its anticoagulant role, its effects on energy homeostasis are unknown. Here, we demonstrate that heparin level is negatively associated with nutritional states and that heparin treatment increases food intake and body weight gain. By using electrophysiological, pharmacological, molecular biological, and chemogenetic approaches, we provide evidence that heparin increases food intake by stimulating AgRP neurons and increasing AgRP release. Our results support a model whereby heparin competes with insulin for insulin receptor binding on AgRP neurons, and by doing so it inhibits FoxO1 activity to promote AgRP release and feeding. Heparin may be a potential drug target for food intake regulation and body weight control.
Keywords: AgRP; food intake; heparin; insulin receptor.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Accili D, and Arden KC (2004). FoxOs at the crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and transformation. Cell 117, 421–426. - PubMed
-
- Allman-Farinelli MA (2011). Obesity and venous thrombosis: a review. Semin. Thromb. Hemost 37, 903–907. - PubMed
-
- Biebermann H, Kühnen P, Kleinau G, and Krude H (2012). The neuroendocrine circuitry controlled by POMC, MSH, and AGRP. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol (203), 47–75.. - PubMed
-
- Bloom MB, Zaw AA, Hoang DM, Mason R, Alban RF, Chung R, Melo N, Volod O, Ley EJ, and Margulies DR (2016). Body mass index strongly impacts the diagnosis and incidence of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in the surgical intensive care unit. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg 80, 398–403. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

