IRF9 Prevents CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion in an Extrinsic Manner during Acute Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Infection
- PMID: 28878077
- PMCID: PMC5660491
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01219-17
IRF9 Prevents CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion in an Extrinsic Manner during Acute Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Infection
Abstract
Effective CD8+ T cell responses play an important role in determining the course of a viral infection. Overwhelming antigen exposure can result in suboptimal CD8+ T cell responses, leading to chronic infection. This altered CD8+ T cell differentiation state, termed exhaustion, is characterized by reduced effector function, upregulation of inhibitory receptors, and altered expression of transcription factors. Prevention of overwhelming antigen exposure to limit CD8+ T cell exhaustion is of significant interest for the control of chronic infection. The transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 9 (IRF9) is a component of type I interferon (IFN-I) signaling downstream of the IFN-I receptor (IFNAR). Using acute infection of mice with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) strain Armstrong, we show here that IRF9 limited early LCMV replication by regulating expression of interferon-stimulated genes and IFN-I and by controlling levels of IRF7, a transcription factor essential for IFN-I production. Infection of IRF9- or IFNAR-deficient mice led to a loss of early restriction of viral replication and impaired antiviral responses in dendritic cells, resulting in CD8+ T cell exhaustion and chronic infection. Differences in the antiviral activities of IRF9- and IFNAR-deficient mice and dendritic cells provided further evidence of IRF9-independent IFN-I signaling. Thus, our findings illustrate a CD8+ T cell-extrinsic function for IRF9, as a signaling factor downstream of IFNAR, in preventing overwhelming antigen exposure resulting in CD8+ T cell exhaustion and, ultimately, chronic infection.IMPORTANCE During early viral infection, overwhelming antigen exposure can cause functional exhaustion of CD8+ T cells and lead to chronic infection. Here we show that the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 9 (IRF9) plays a decisive role in preventing CD8+ T cell exhaustion. Using acute infection of mice with LCMV strain Armstrong, we found that IRF9 limited early LCMV replication by regulating expression of interferon-stimulated genes and Irf7, encoding a transcription factor crucial for type I interferon (IFN-I) production, as well as by controlling the levels of IFN-I. Infection of IRF9-deficient mice led to a chronic infection that was accompanied by CD8+ T cell exhaustion due to defects extrinsic to T cells. Our findings illustrate an essential role for IRF9, as a mediator downstream of IFNAR, in preventing overwhelming antigen exposure causing CD8+ T cell exhaustion and leading to chronic viral infection.
Keywords: CD8+ T cell exhaustion; interferon regulatory factor 9; lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus; type I interferon.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
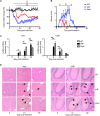
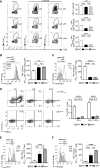

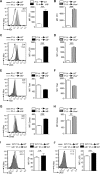
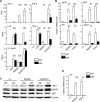
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

