Effects of Intensive Blood Pressure Reduction on Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 28878305
- PMCID: PMC5587814
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-10892-z
Effects of Intensive Blood Pressure Reduction on Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Current opinions about the effect of intensive blood pressure (BP) reduction for acute intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) are inconsistent. We performed a meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy and safety of intensive BP reduction for acute ICH by analyzing data from several recent randomized controlled trials (RCTs). There were six eligible studies that met the inclusion criteria, for a total of 4,385 acute ICH patients in this meta-analysis. After analyzing these data, we found differences between intensive and standard BP lowering treatment groups in total mortality rates, unfavorable outcomes, hematoma expansion, neurologic deterioration, and severe hypotension were not significant. Moreover, compared with the standard treatment, the rate of renal adverse event in intensive treatment group was significantly higher. The intensive treatment approach was recommended in the following situations: (1) longer prehospital duration; (2) lower National Institute of Health stroke scale (NIHSS) score; (3) no hypertension history.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



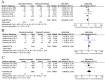
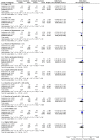
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

