Prognostic relevance of an epigenetic biomarker panel in sentinel lymph nodes from colon cancer patients
- PMID: 28878843
- PMCID: PMC5584052
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-017-0397-4
Prognostic relevance of an epigenetic biomarker panel in sentinel lymph nodes from colon cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Patients with early colorectal cancer (stages I-II) generally have a good prognosis, but a subgroup of 15-20% experiences relapse and eventually die of disease. Occult metastases have been suggested as a marker for increased risk of recurrence in patients with node-negative disease. Using a previously identified, highly accurate epigenetic biomarker panel for early detection of colorectal tumors, we aimed at evaluating the prognostic value of occult metastases in sentinel lymph nodes of colon cancer patients.
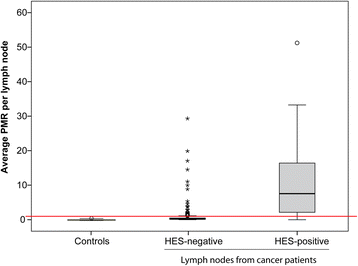
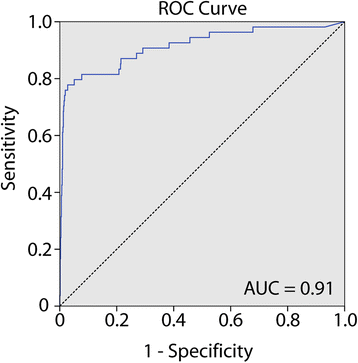
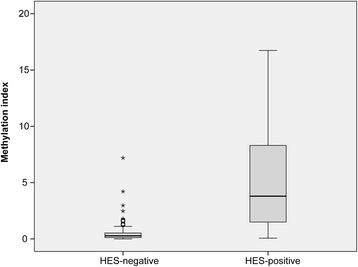
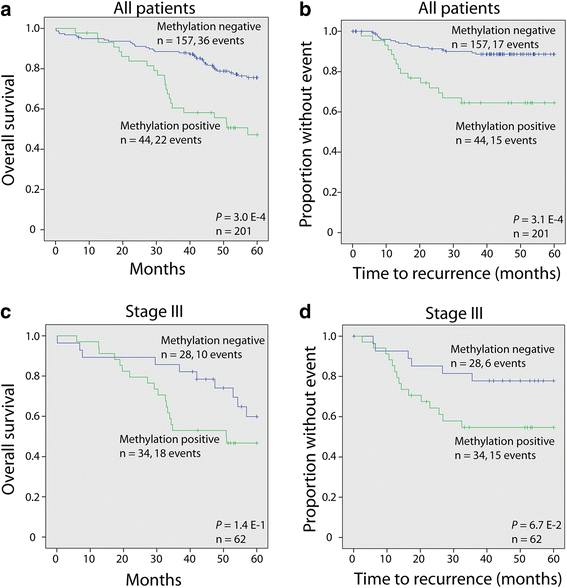
Results: The biomarker panel was analyzed by quantitative methylation-specific PCR in primary tumors and 783 sentinel lymph nodes from 201 patients. The panel status in sentinel lymph nodes showed a strong association with lymph node stage (P = 8.2E-17). Compared with routine lymph node diagnostics, the biomarker panel had a sensitivity of 79% (31/39). Interestingly, among 162 patients with negative lymph nodes from routine diagnostics, 13 (8%) were positive for the biomarker panel. Colon cancer patients with high sentinel lymph node methylation had an inferior prognosis (5-year overall survival P = 3.0E-4; time to recurrence P = 3.1E-4), although not significant. The same trend was observed in multivariate analyses (P = 1.4E-1 and P = 6.7E-2, respectively). Occult sentinel lymph node metastases were not detected in early stage (I-II) colon cancer patients who experienced relapse.
Conclusions: Colon cancer patients with high sentinel lymph node methylation of the analyzed epigenetic biomarker panel had an inferior prognosis, although not significant in multivariate analyses. Occult metastases in TNM stage II patients that experienced relapse were not detected.
Keywords: Biomarkers; DNA methylation; Occult metastases; Prognosis; Relapse; Sentinel lymph nodes.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Informed written consent was obtained from all patients, and the study was approved by the Regional Committees for Medical and Health Research Ethics (REC 197.04). All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

