Neighborhood Influences on Vehicle-Pedestrian Crash Severity
- PMID: 28879440
- PMCID: PMC5722732
- DOI: 10.1007/s11524-017-0200-z
Neighborhood Influences on Vehicle-Pedestrian Crash Severity
Abstract
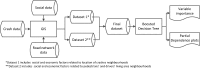
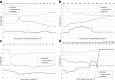
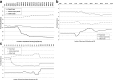
Socioeconomic factors are known to be contributing factors for vehicle-pedestrian crashes. Although several studies have examined the socioeconomic factors related to the location of the crashes, limited studies have considered the socioeconomic factors of the neighborhood where the road users live in vehicle-pedestrian crash modelling. This research aims to identify the socioeconomic factors related to both the neighborhoods where the road users live and where crashes occur that have an influence on vehicle-pedestrian crash severity. Data on vehicle-pedestrian crashes that occurred at mid-blocks in Melbourne, Australia, was analyzed. Neighborhood factors associated with road users' residents and location of crash were investigated using boosted regression tree (BRT). Furthermore, partial dependence plots were applied to illustrate the interactions between these factors. We found that socioeconomic factors accounted for 60% of the 20 top contributing factors to vehicle-pedestrian crashes. This research reveals that socioeconomic factors of the neighborhoods where the road users live and where the crashes occur are important in determining the severity of the crashes, with the former having a greater influence. Hence, road safety countermeasures, especially those focussing on the road users, should be targeted at these high-risk neighborhoods.
Keywords: Boosted regression tree; Neighborhood socioeconomic influences; Neighborhood where crash occur; Neighborhoods where road users live; Vehicle-pedestrian crashes.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hierarchical ordered model for injury severity of pedestrian crashes in South Korea.J Safety Res. 2017 Jun;61:33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jsr.2017.02.011. Epub 2017 Mar 6. J Safety Res. 2017. PMID: 28454869
-
Influence of pedestrian age and gender on spatial and temporal distribution of pedestrian crashes.Traffic Inj Prev. 2018 Jan 2;19(1):81-87. doi: 10.1080/15389588.2017.1341630. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Traffic Inj Prev. 2018. PMID: 28605251
-
Walking under the influence of the alcohol: A case study of pedestrian crashes in Tennessee.Accid Anal Prev. 2018 Dec;121:64-70. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Accid Anal Prev. 2018. PMID: 30223082
-
Macro-level vulnerable road users crash analysis: A Bayesian joint modeling approach of frequency and proportion.Accid Anal Prev. 2017 Oct;107:11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.aap.2017.07.020. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Accid Anal Prev. 2017. PMID: 28753415 Review.
-
Analysis of risk factors affecting driver injury and crash injury with drivers under the influence of alcohol (DUI) and non-DUI.Traffic Inj Prev. 2016 Nov 16;17(8):796-802. doi: 10.1080/15389588.2016.1168924. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Traffic Inj Prev. 2016. PMID: 27064506 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlates of the Built Environment and Active Travel: Evidence from 20 US Metropolitan Areas.Environ Health Perspect. 2018 Jul 30;126(7):077011. doi: 10.1289/EHP3389. eCollection 2018 Jul. Environ Health Perspect. 2018. PMID: 30073954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Global status report on road safety 2015. Geneva , Switzerland: World Health Organization, Department of Violence & Injury Prevention & Disability (VIP). 2015
-
- Rifaat S, Tay R, Perez A, Barros AD. Effects of neighborhood street patterns on traffic collision frequency. J Transp Safety & Security. 2009;1(4):241–253. doi: 10.1080/19439960903328595. - DOI
-
- Rifaat SM, Tay R, de Barros A. Urban street pattern and pedestrian traffic safety. J Urban Design. 2012;17(3):337–352. doi: 10.1080/13574809.2012.683398. - DOI
-
- Li D, Ranjitkar P, Zhao Y, Yi H, Rashidi S. Analyzing pedestrian crash injury severity under different weather conditions. Traffic Inj Prev. 2016:00–0. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

