Clinical grade manufacturing of genetically modified, CAR-expressing NK-92 cells for the treatment of ErbB2-positive malignancies
- PMID: 28879551
- PMCID: PMC11028154
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-017-2055-2
Clinical grade manufacturing of genetically modified, CAR-expressing NK-92 cells for the treatment of ErbB2-positive malignancies
Abstract
Background: The NK-92/5.28.z cell line (also referred to as HER2.taNK) represents a stable, lentiviral-transduced clone of ErbB2 (HER2)-specific, second-generation CAR-expressing derivative of clinically applicable NK-92 cells. This study addresses manufacturing-related issues and aimed to develop a GMP-compliant protocol for the generation of NK-92/5.28.z therapeutic doses starting from a well-characterized GMP-compliant master cell bank.
Materials and methods: Commercially available GMP-grade culture media and supplements (fresh frozen plasma, platelet lysate) were evaluated for their ability to support expansion of NK-92/5.28.z. Irradiation sensitivity and cytokine release were also investigated.
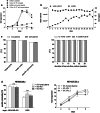
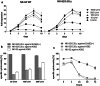
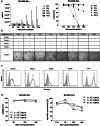
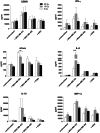
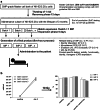
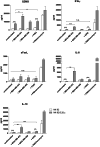
Results: NK-92/5.28.z cells can be grown to clinically applicable cell doses of 5 × 108 cells/L in a 5-day batch culture without loss of viability and potency. X-Vivo 10 containing recombinant transferrin supplemented with 5% FFP and 500 IU/mL IL-2 in VueLife 750-C1 bags showed the best results. Platelet lysate was less suited to support NK-92/5.28.z proliferation. Irradiation with 10 Gy completely abrogated NK-92/5.28.z proliferation and preserved viability and potency for at least 24 h. NK-92/5.28.z showed higher baseline cytokine release compared to NK-92, which was significantly increased upon encountering ErbB2(+) targets [GZMB (twofold), IFN-γ (fourfold), IL-8 (24-fold) and IL-10 (fivefold)]. IL-6 was not released by NK cells, but was observed in some stimulated targets. Irradiation resulted in upregulation of IL-8 and downregulation of sFasL, while other cytokines were not impacted.
Conclusion: Our concept suggests NK-92/5.28.z maintenance culture from which therapeutic doses up to 5 × 109 cells can be expanded in 10 L within 5 days. This established process is feasible to analyze NK-92/5.28.z in phase I/II trials.
Keywords: CAR; Cancer immunotherapy; Glioblastoma; HER2; NK-92; Natural killer cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimization of Human NK Cell Manufacturing: Fully Automated Separation, Improved Ex Vivo Expansion Using IL-21 with Autologous Feeder Cells, and Generation of Anti-CD123-CAR-Expressing Effector Cells.Hum Gene Ther. 2017 Oct;28(10):897-913. doi: 10.1089/hum.2017.157. Epub 2017 Aug 15. Hum Gene Ther. 2017. PMID: 28810809
-
NK-92: an 'off-the-shelf therapeutic' for adoptive natural killer cell-based cancer immunotherapy.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2016 Apr;65(4):485-92. doi: 10.1007/s00262-015-1761-x. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2016. PMID: 26559813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective inhibition of tumor growth by clonal NK cells expressing an ErbB2/HER2-specific chimeric antigen receptor.Mol Ther. 2015 Feb;23(2):330-8. doi: 10.1038/mt.2014.219. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Mol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25373520 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Clinical Manufacturing of IL-15 Activated Cytokine-Induced Killer (CIK) Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 May 31;10:1218. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01218. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31214182 Free PMC article.
-
CAR-NK Cells: From Natural Basis to Design for Kill.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 14;12:707542. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.707542. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34970253 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Anti-tumor Function through Advanced Media Design.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020 Jul 9;18:595-606. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2020.07.008. eCollection 2020 Sep 11. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020. PMID: 32775494 Free PMC article.
-
Current Perspectives on the Use of off the Shelf CAR-T/NK Cells for the Treatment of Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 16;13(8):1926. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081926. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33923528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retroviral gene therapy in Germany with a view on previous experience and future perspectives.Gene Ther. 2021 Sep;28(9):494-512. doi: 10.1038/s41434-021-00237-x. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Gene Ther. 2021. PMID: 33753908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current status and future perspective of natural killer cell therapy for cancer.Med Rev (2021). 2023 Oct 24;3(4):305-320. doi: 10.1515/mr-2023-0031. eCollection 2023 Aug. Med Rev (2021). 2023. PMID: 38235405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Cancer Potential of Transiently Transfected HER2-Specific Human Mixed CAR-T and NK Cell Populations in Experimental Models: Initial Studies on Fucosylated Chondroitin Sulfate Usage for Safer Treatment.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 18;11(9):2563. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092563. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37761005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Esser R, Muller T, Stefes D, Kloess S, Seidel D, Gillies SD, et al. NK cells engineered to express a GD2 -specific antigen receptor display built-in ADCC-like activity against tumour cells of neuroectodermal origin. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16:569–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01343.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Genssler S, Burger MC, Zhang C, Oelsner S, Mildenberger I, Wagner M, et al. Dual targeting of glioblastoma with chimeric antigen receptor-engineered natural killer cells overcomes heterogeneity of target antigen expression and enhances antitumor activity and survival. Oncoimmunology. 2016;5:e1119354. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1119354. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 131A009A/German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) Cluster für individualisierte Immunintervention, Ci3/International
- 131A009B/German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) Cluster für individualisierte Immunintervention, Ci3/International
- 131A009C/German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) Cluster für individualisierte Immunintervention, Ci3/International
- III L 5-518/17.004/LOEWE Center for Cell and Gene Therapy Frankfurt (CGT)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

