Dual-Mode Electro-Optical Techniques for Biosensing Applications: A Review
- PMID: 28880211
- PMCID: PMC5620729
- DOI: 10.3390/s17092047
Dual-Mode Electro-Optical Techniques for Biosensing Applications: A Review
Abstract
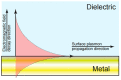
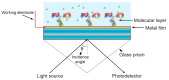
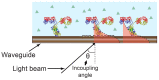
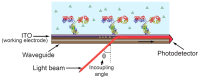
The monitoring of biomolecular interactions is a key requirement for the study of complex biological processes and the diagnosis of disease. Technologies that are capable of providing label-free, real-time insight into these interactions are of great value for the scientific and clinical communities. Greater understanding of biomolecular interactions alongside increased detection accuracy can be achieved using technology that can provide parallel information about multiple parameters of a single biomolecular process. For example, electro-optical techniques combine optical and electrochemical information to provide more accurate and detailed measurements that provide unique insights into molecular structure and function. Here, we present a comparison of the main methods for electro-optical biosensing, namely, electrochemical surface plasmon resonance (EC-SPR), electrochemical optical waveguide lightmode spectroscopy (EC-OWLS), and the recently reported silicon-based electrophotonic approach. The comparison considers different application spaces, such as the detection of low concentrations of biomolecules, integration, the tailoring of light-matter interaction for the understanding of biomolecular processes, and 2D imaging of biointeractions on a surface.
Keywords: electro-optical devices; label-free detection; optical biosensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

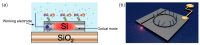
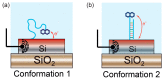
References
-
- Sharma R., Deacon S.E., Nowak D., George S.E., Szymonik M.P., Tang A.A.S., Tomlinson D.C., Davies A.G., McPherson M.J., Walti C. Label-free electrochemical impedance biosensor to detect human interleukin-8 in serum with sub-pg/ml sensitivity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016;80:607–613. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.02.028. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

