Staphylococcal enterotoxin-like X (SElX) is a unique superantigen with functional features of two major families of staphylococcal virulence factors
- PMID: 28880913
- PMCID: PMC5589262
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006549
Staphylococcal enterotoxin-like X (SElX) is a unique superantigen with functional features of two major families of staphylococcal virulence factors
Abstract
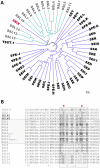
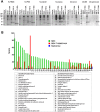
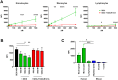
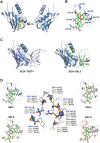
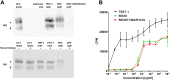
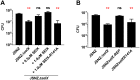
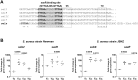
Staphylococcus aureus is an opportunistic pathogen that produces many virulence factors. Two major families of which are the staphylococcal superantigens (SAgs) and the Staphylococcal Superantigen-Like (SSL) exoproteins. The former are immunomodulatory toxins that induce a Vβ-specific activation of T cells, while the latter are immune evasion molecules that interfere with a wide range of innate immune defences. The superantigenic properties of Staphylococcal enterotoxin-like X (SElX) have recently been established. We now reveal that SElX also possesses functional characteristics of the SSLs. A region of SElX displays high homology to the sialyl-lactosamine (sLacNac)-specific binding site present in a sub-family of SSLs. By analysing the interaction of SElX with sLacNac-containing glycans we show that SElX has an equivalent specificity and host cell binding range to the SSLs. Mutation of key amino acids in this conserved region affects the ability of SElX to bind to cells of myeloid origin and significantly reduces its ability to protect S. aureus from destruction in a whole blood killing (WBK) assay. Like the SSLs, SElX is up-regulated early during infection and is under the control of the S. aureus exotoxin expression (Sae) two component gene regulatory system. Additionally, the structure of SElX in complex with the sLacNac-containing tetrasaccharide sialyl Lewis X (sLeX) reveals that SElX is a unique single-domain SAg. In summary, SElX is an 'SSL-like' SAg.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no financial, personal, or professional interests that could be construed to have influenced this work.
Figures


References
-
- Tong SC, Chen L, Fowler V Jr. Colonization, pathogenicity, host susceptibility, and therapeutics for Staphylococcus aureus: what is the clinical relevance? Seminars in Immunopathology. 2012;34(2):185–200. doi: 10.1007/s00281-011-0300-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Williamson DA, Heffernan H. The changing landscape of antimicrobial resistance in New Zealand. N Z Med J. 2014;127(1403):41–54. - PubMed
-
- Wertheim HF, Melles DC, Vos MC, van Leeuwen W, van Belkum A, Verbrugh HA, et al. The role of nasal carriage in Staphylococcus aureus infections. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5(12):751–62. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(05)70295-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- von Eiff C, Becker K, Machka K, Stammer H, Peters G. Nasal Carriage as a Source of Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia. New England Journal of Medicine. 2001;344(1):11–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200101043440102 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wertheim HF, Vos MC, Ott A, van Belkum A, Voss A, Kluytmans JA, et al. Risk and outcome of nosocomial Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia in nasal carriers versus non-carriers. Lancet. 2004;364(9435):703–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

