Identification of CEA-interacting proteins in colon cancer cells and their changes in expression after irradiation
- PMID: 28881503
- PMCID: PMC5654139
- DOI: 10.3857/roj.2017.00255
Identification of CEA-interacting proteins in colon cancer cells and their changes in expression after irradiation
Abstract
Purpose: The serum carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) level has been recognized as a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer, and associated with response of rectal cancer to radiotherapy. This study aimed to identify CEA-interacting proteins in colon cancer cells and observe post-irradiation changes in their expression.
Materials and methods: CEA expression in colon cancer cells was examined by Western blot analysis. Using an anti-CEA antibody or IgG as a negative control, immunoprecipitation was performed in colon cancer cell lysates. CEA and IgG immunoprecipitates were used for liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis. Proteins identified in the CEA immunoprecipitates but not in the IgG immunoprecipitates were selected as CEA-interacting proteins. After radiation treatment, changes in expression of CEA-interacting proteins were monitored by Western blot analysis.
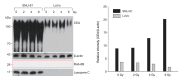
Results: CEA expression was higher in SNU-81 cells compared with LoVo cells. The membrane localization of CEA limited the immunoprecipitation results and thus the number of CEA-interacting proteins identified. Only the Ras-related protein Rab-6B and lysozyme C were identified as CEA-interacting proteins in LoVo and SNU-81 cells, respectively. Lysozyme C was detected only in SNU-81, and CEA expression was differently regulated in two cell lines; it was down-regulated in LoVo but up-regulated in SNU-81 in radiation dosage-dependent manner.
Conclusion: CEA-mediated radiation response appears to vary, depending on the characteristics of individual cancer cells. The lysozyme C and Rab subfamily proteins may play a role in the link between CEA and tumor response to radiation, although further studies are needed to clarify functional roles of the identified proteins.
Keywords: Carcinoembryonic antigen; Colorectal neoplasms; Lysozyme C; Rab-6B; Radiation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



References
-
- Beauchemin N, Draber P, Dveksler G, et al. Redefined nomenclature for members of the carcinoembryonic antigen family. Exp Cell Res. 1999;252:243–9. - PubMed
-
- Thomas P, Toth CA, Saini KS, Jessup JM, Steele G Jr. The structure, metabolism and function of the carcinoembryonic antigen gene family. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990;1032:177–89. - PubMed
-
- Hammarstrom S. The carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) family: structures, suggested functions and expression in normal and malignant tissues. Semin Cancer Biol. 1999;9:67–81. - PubMed
-
- Thomas P, Forse RA, Bajenova O. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and its receptor hnRNP M are mediators of metastasis and the inflammatory response in the liver. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2011;28:923–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources