PD1 signal transduction pathways in T cells
- PMID: 28881701
- PMCID: PMC5584302
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17232
PD1 signal transduction pathways in T cells
Abstract
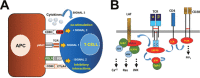
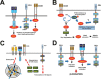
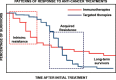
The use of immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of cancer is revolutionizing oncology. Amongst these therapeutic agents, antibodies that block PD-L1/PD1 interactions between cancer cells and T cells are demonstrating high efficacies and low toxicities. Despite all the recent advances, very little is yet known on the molecular intracellular signaling pathways regulated by either PD-L1 or PD1. Here we review the current knowledge on PD1-dependent intracellular signaling pathways, and the consequences of disrupting PD1 signal transduction.
Keywords: B7-H1; PD-L1; PD1; PDL1; cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gato-Cañas M, Arasanz H, Blanco-Luquin I, Glaría E, Arteta-Sanchez V, Kochan G, Escors D. Novel immunotherapies for the treatment of melanoma. Immunotherapy. 2016;8:613–32. - PubMed
-
- Sharpe AH, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R, Freeman GJ. The function of programmed cell death 1 and its ligands in regulating autoimmunity and infection. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:239–45. - PubMed
-
- Curtsinger JM, Johnson CM, Mescher MF. CD8 T cell clonal expansion and development of effector function require prolonged exposure to antigen, costimulation, and signal 3 cytokine. J Immunol. 2003;171:5165–71. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

