New use of low-dose aspirin and risk of colorectal cancer by stage at diagnosis: a nested case-control study in UK general practice
- PMID: 28882113
- PMCID: PMC5590216
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3594-9
New use of low-dose aspirin and risk of colorectal cancer by stage at diagnosis: a nested case-control study in UK general practice
Abstract
Background: Evidence from clinical trial populations suggests low-dose aspirin reduces the risk of colorectal cancer (CRC). Part of this reduction in risk might be due to protection against metastatic disease.
Methods: We investigated the risk of CRC among new-users of low-dose aspirin (75-300 mg), including risk by stage at diagnosis. Using The Health Improvement Network, we conducted a cohort study with nested case-control analysis. Two cohorts (N = 170,336 each) aged 40-89 years from 2000 to 2009 and free of cancer were identified: i) new-users of low-dose aspirin, ii) non-users of low-dose aspirin, at start of follow-up, matched by age, sex and previous primary care practitioner visits. Patients were followed for up to 12 years to identify incident CRC. 10,000 frequency-matched controls were selected by incidence density sampling where the odds ratio is an unbiased estimator of the incidence rate ratio (RR). RRs with 95% confidence intervals were calculated. Low-dose aspirin use was classified 'as-treated' independent from baseline exposure status to account for changes in exposure during follow-up.
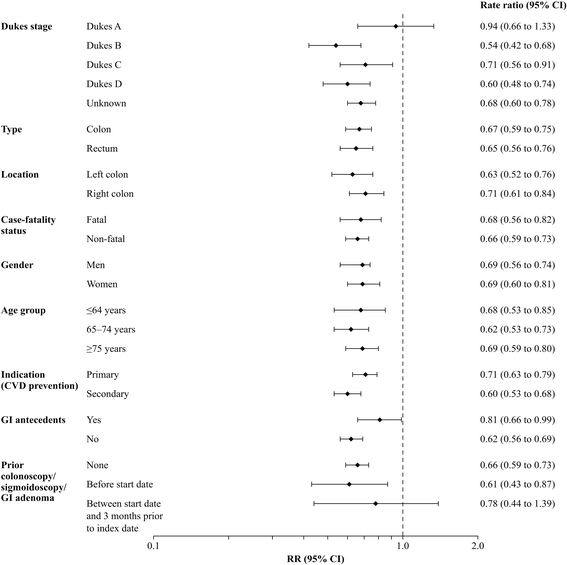
Results: Current users of low-dose aspirin (use on the index date or in the previous 90 days) had a significantly reduced risk of CRC, RR 0.66 (95% CI 0.60-0.74). The reduction in risk was apparent across all age groups, and was unrelated to dose, indication, gender, CRC location or case-fatality status. Reduced risks occurred throughout treatment duration and with all low-dose aspirin doses. RRs by aspirin indication were 0.71 (0·63-0·79) and 0.60 (0.53-0.68) for primary and secondary cardiovascular protection, respectively. Among cases with staging information (n = 1421), RRs for current use of low-dose aspirin were 0.94 (0.66-1.33) for Dukes Stage A CRC, 0.54 (0.42-0.68) for Dukes B, 0.71 (0.56-0.91) for Dukes C, and 0.60 (0.48-0.74) for Dukes D. After 5 years' therapy, the RR for Dukes Stage A CRC was 0.53 (0.24-1.19).
Conclusions: Patients starting low-dose aspirin therapy have a reduced risk of Stages B-D CRC, suggesting a role for low-dose aspirin in the progression of established CRC; a substantial reduction in the risk of Dukes A CRC may occur after 5 years' therapy.
Keywords: Aspirin; Chemoprevention; Colorectal cancer; Diagnosis; Nested case-control studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was reviewed and approved by an independent scientific review committee for THIN (reference number 14–080), which ensured that data were to be analysed and interpreted appropriately. Data collection for THIN was approved by the South East Multicentre Research Ethics Committee in 2003 and individual studies using THIN data do not require separate ethical approval if only anonymized THIN data is used (CSD Health Research. MREC.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
MS-G is a salaried, full-time employee of Bayer AG. LCS and LAGR work for CEIFE, which has received a research grant from Bayer AG. LAGR has also served as an advisory board member for Bayer AG. SB has received funding from Bayer AG for epidemiological research and medical writing services. AL has received a research grant from Bayer AG and has served as an advisory board member for Bayer AG and Bayer HealthCare.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik MFerlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: IARC CancerBase no. 11 [internet] International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon; 2013.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

