Short-term administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide preserves cardiac mitochondrial homeostasis and prevents heart failure
- PMID: 28882480
- PMCID: PMC6257991
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.09.001
Short-term administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide preserves cardiac mitochondrial homeostasis and prevents heart failure
Abstract
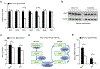
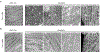
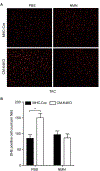
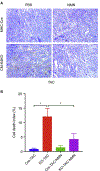
Heart failure is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction so that restoring or improving mitochondrial health is of therapeutic importance. Recently, reduction in NAD+ levels and NAD+-mediated deacetylase activity has been recognized as negative regulators of mitochondrial function. Using a cardiac specific KLF4 deficient mouse line that is sensitive to stress, we found mitochondrial protein hyperacetylation coupled with reduced Sirt3 and NAD+ levels in the heart before stress, suggesting that the KLF4-deficient heart is predisposed to NAD+-associated defects. Further, we demonstrated that short-term administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) successfully protected the mutant mice from pressure overload-induced heart failure. Mechanically, we showed that NMN preserved mitochondrial ultrastructure, reduced ROS and prevented cell death in the heart. In cultured cardiomyocytes, NMN treatment significantly increased long-chain fatty acid oxidation despite no direct effect on pyruvate oxidation. Collectively, these results provide cogent evidence that hyperacetylation of mitochondrial proteins is critical in the pathogenesis of cardiac disease and that administration of NMN may serve as a promising therapy.
Keywords: Heart failure; Mitochondria; NAD; Pressure overload; Protein hyperacetylation.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


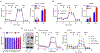
References
-
- Lopaschuk GD, Ussher JR, Folmes CD, Jaswal JS, Stanley WC, Myocardial fatty acid metabolism in health and disease, Physiol. Rev 90 (1) (2010) 207–258. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

