Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction and Orthostatic Hypotension Associated with Small Cell Lung Cancer that Improved with Tumor Reduction after Chemoradiotherapy
- PMID: 28883237
- PMCID: PMC5658530
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8574-16
Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction and Orthostatic Hypotension Associated with Small Cell Lung Cancer that Improved with Tumor Reduction after Chemoradiotherapy
Abstract
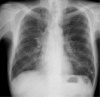
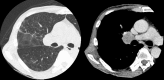
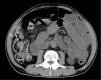
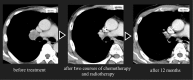
Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIPO) is a rare disease with symptoms of ileus without obstruction. Most cases of CIPO are idiopathic, and CIPO as a paraneoplastic neurological syndrome (PNS) associated with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is rare. A 63-year-old man was diagnosed with functional ileus and confined to bed due to orthostatic hypotension. Chest computed tomography revealed a right hilar mass suspected of being lung cancer. Based on detailed examinations, he was diagnosed with limited-stage SCLC. His symptoms were confirmed as PNS because his serum anti-Hu antibody was positive. His PNS was improved with complete tumor reduction by chemoradiotherapy.
Keywords: anti-Hu antibody; chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction; orthostatic hypotension; paraneoplastic neurological syndrome; small cell lung cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Iida H, Inamori M, Sekino Y, Sakamoto Y, Yamato S, Nakajima A. A review of the reported cases of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in Japan and an investigation of proposed new diagnostic criteria. Clin J Gastroenterol 4: 141-146, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Vedeler CA, Antoine JC, Giometto B, et al. . Management of paraneoplastic neurological syndromes: report of an EFNS Task Force. Eur J Neurol 13: 682-690, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Lucchinetti CF, Kimmel DW, Lennon VA. Paraneoplastic and oncologic profiles of patients seropositive for type 1 antineuronal nuclear autoantibodies. Neurology 50: 652-657, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Lee HR, Lennon VA, Camilleri M, Prather CM. Paraneoplastic gastrointestinal motor dysfunction: clinical and laboratory characteristics. Am J Gastroenterol 96: 373-379, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

