Metabolic heterogeneity of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomic study
- PMID: 28883924
- PMCID: PMC5531310
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjresp-2017-000183
Metabolic heterogeneity of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomic study
Abstract
Introduction: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic and fatal disease of unknown cause characterised by progressive fibrotic formation in lung tissue. We hypothesise that disrupted metabolic pathways in IPF contribute to disease pathogenesis.
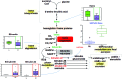
Methods: Metabolomics of human IPF was performed using mass spectroscopy (IPF lung=8; donor lung=8). Gene expression of key metabolic enzymes was measured using microarrays. Of the 108 metabolites whose levels were found altered, 48 were significantly increased, whereas 60 were significantly decreased in IPF samples compared with normal controls.
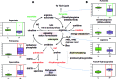
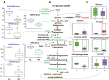
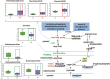
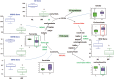
Results: Specific metabolic pathways mediating the IPF remodelling were found with a downregulated sphingolipid metabolic pathway but an upregulated arginine pathway in IPF. In addition, disrupted glycolysis, mitochondrial beta-oxidation and tricarboxylic acid cycle, altered bile acid, haem and glutamate/aspartate metabolism were found in IPF samples compared with control.
Conclusions: Our results show alterations in metabolic pathways for energy consumption during lung structural remodelling, which may contribute to IPF pathogenesis. We believe that this is the first report of simultaneously and systemically measuring changes of metabolites involving nine metabolic pathways in human severe IPF lungs. The measurement of the metabolites may serve in the future diagnosis and prognosis of IPF.
Keywords: interstitial fibrosis; lung transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Kekevian A, Gershwin ME, Chang C. Diagnosis and classification of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Autoimmun Rev 2014;13:508–12.doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2014.01.037 - DOI - PubMed
-
- King TE, Pardo A, Selman M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2011;378:1949–61.doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60052-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wolters PJ, Collard HR, Jones KD. Pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol 2014;9:157–79.doi:10.1146/annurev-pathol-012513-104706 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chambers RC, Scotton CJ. Coagulation cascade proteinases in lung injury and fibrosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2012;9:96–101.doi:10.1513/pats.201201-006AW - DOI - PubMed
-
- Camera L, Campanile F, Imbriaco M, et al. . Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis complicated by acute thromboembolic disease: chest X-ray, HRCT and multi-detector row CT angiographic findings. J Thorac Dis 2013;5:82–6.doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2012.12.03 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
