Obesity and kidney disease: hidden consequences of the epidemic
- PMID: 28883987
- PMCID: PMC5583661
- DOI: 10.4155/fsoa-2016-0081
Obesity and kidney disease: hidden consequences of the epidemic
Abstract
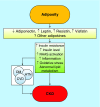
Obesity has become a worldwide epidemic, and its prevalence has been projected to grow by 40% in the next decade. This increasing prevalence has implications for the risk of diabetes, cardiovascular disease and also for chronic kidney disease. A high BMI is one of the strongest risk factors for new-onset chronic kidney disease. In individuals affected by obesity, a compensatory hyperfiltration occurs to meet the heightened metabolic demands of the increased body weight. The increase in intraglomerular pressure can damage the kidneys and raise the risk of developing chronic kidney disease in the long-term. The incidence of obesity-related glomerulopathy has increased tenfold in recent years. Obesity has also been shown to be a risk factor for nephrolithiasis, and for a number of malignancies including kidney cancer. This year the World Kidney Day promotes education on the harmful consequences of obesity and its association with kidney disease, advocating healthy lifestyle and health policy measures that make preventive behaviors an affordable option.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; kidney cancer; nephrolithiasis; obesity; prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial & competing interests disclosure The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Obesity and Kidney Disease: Hidden Consequences of the Epidemic.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2017 Jul;3(1):33-41. doi: 10.1159/000452965. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28785562 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and Kidney Disease: Hidden Consequences of the Epidemic.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2017 Mar 8;4:2054358117698669. doi: 10.1177/2054358117698669. eCollection 2017. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28540059 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and kidney disease: hidden consequences of the epidemic.Clin Kidney J. 2017 Feb;10(1):1-8. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfw139. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Clin Kidney J. 2017. PMID: 28638599 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and kidney disease: hidden consequences of the epidemic.J Nephrol. 2017 Feb;30(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s40620-017-0377-y. J Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28214961 Review.
-
Obesity and kidney disease: hidden consequences of the epidemic.J Bras Nefrol. 2017 Mar;39(1):1-10. doi: 10.5935/0101-2800.20170001. J Bras Nefrol. 2017. PMID: 28355410 Review. English, Portuguese.
Cited by
-
Overweight among seafarers working on board merchant ships.BMC Public Health. 2019 Jan 9;19(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-6377-6. BMC Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30626365 Free PMC article.
-
Early triggers of moderately high-fat diet-induced kidney damage.Physiol Rep. 2021 Jul;9(14):e14937. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14937. Physiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34291592 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological Outcomes and Predictors of Weight Loss in Adolescents With Severe Obesity Following a Reversible Endoscopic Bariatric Procedure.Front Pediatr. 2021 Jun 4;9:688287. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.688287. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34178903 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of the Food Supplement Flexovital in a Model of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome in Mice.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 28;16(23):4105. doi: 10.3390/nu16234105. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39683499 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal study of glomerular hyperfiltration and normalization of estimated glomerular filtration in adults with sickle cell disease.Br J Haematol. 2021 Oct;195(1):123-132. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17723. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Br J Haematol. 2021. PMID: 34402052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forouzanfar MH, Alexander L, Anderson HR, et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386:2287–2323. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cattaneo A, Monasta L, Stamatakis E, et al. Overweight and obesity in infants and pre-school children in the European Union: a review of existing data. Obes. Rev. 2010;11:389–398. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
