Inhibition of IKK-NFκB pathway sensitizes lung cancer cell lines to radiation
- PMID: 28884046
- PMCID: PMC5570606
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2017.0049
Inhibition of IKK-NFκB pathway sensitizes lung cancer cell lines to radiation
Abstract
Objective: : Cancer cell radioresistance is a stumbling block in radiation therapy. The activity in the nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) pathway correlates with anti-apoptotic mechanisms and increased radioresistance. The IKK complex plays a major role in NFκB activation upon numerous signals. In this study, we examined the interaction between ionizing radiation (IR) and different members of the IKK-NFκB pathway, as well as upstream activators, RAF1, ERK, and AKT1.
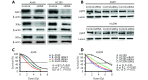
Methods: : The effect of 4 Gy of IR on the expression of the RAF1-ERK-IKK-NFκB pathway was examined in A549 and H1299 lung cancer cell lines using Western blot analysis and confocal microscopy. We examined changes in radiation sensitivity using gene silencing or pharmacological inhibitors of ERK and IKKβ.
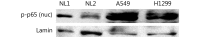
Results: : IKKα, IKKγ, and IκBα increased upon exposure to IR, thereby affecting nuclear levels of NFκB (phospho-p65). ERK inhibition or siRNA-mediated down-regulation of RAF1 suppressed the post-irradiation survival of the examined lung cancer cell lines. A similar effect was detected on survival upon silencing IKKα/IKKγ or inhibiting IKKβ.
Conclusions: : Exposure of lung cancer cells to IR results in NFκB activation via IKK. The genetic or pharmacological blockage of the RAF1-ERK-IKK-NFκB pathway sensitizes cells to therapeutic doses of radiation. Therefore, the IKK pathway is a promising target for therapeutic intervention in combination with radiotherapy.
Keywords: IKK; NFκΒ; ionising radiation; lung cancer; radiosensitization.
Figures



Similar articles
-
IKKβ regulates the repair of DNA double-strand breaks induced by ionizing radiation in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 7;6(4):e18447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018447. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21490922 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
The role of intracellular Ca2+ in the regulation of proteinase-activated receptor-2 mediated nuclear factor kappa B signalling in keratinocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Jun;145(4):535-44. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706204. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15821758 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming adaptive resistance in mucoepidermoid carcinoma through inhibition of the IKK-β/IκBα/NFκB axis.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 8;7(45):73032-73044. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12195. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27682876 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin: it's role in regulation of cell motility and nuclear factor kappa B-mediated urokinase type plasminogen activator expression.IUBMB Life. 2005 Jun;57(6):441-7. doi: 10.1080/15216540500159424. IUBMB Life. 2005. PMID: 16012053 Review.
Cited by
-
Ginsenoside Rg5 enhances the radiosensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma via reducing HSP90-CDC37 interaction and promoting client protein degradation.J Pharm Anal. 2023 Nov;13(11):1296-1308. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.06.004. Epub 2023 Jun 7. J Pharm Anal. 2023. PMID: 38174116 Free PMC article.
-
Genes Involved in the PD-L1 Pathway Might Associate with Radiosensitivity of Patients with Gastric Cancer.J Oncol. 2020 Sep 8;2020:7314195. doi: 10.1155/2020/7314195. eCollection 2020. J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32963532 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the CREB Protein Family Members and the Related Transcription Factors in Radioresistance Mechanisms.Life (Basel). 2021 Dec 20;11(12):1437. doi: 10.3390/life11121437. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34947968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pentoxifylline Sensitizes Cisplatin-Resistant Human Cervical Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Treatment: Involvement of Mitochondrial and NF-Kappa B Pathways.Front Oncol. 2020 Dec 16;10:592706. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.592706. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33680921 Free PMC article.
-
Review: Mechanisms and perspective treatment of radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 14;14:1133899. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1133899. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36865554 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
