Podophyllotoxin: a novel potential natural anticancer agent
- PMID: 28884079
- PMCID: PMC5580867
Podophyllotoxin: a novel potential natural anticancer agent
Abstract
Objective: The aim of the present review is to give an overview about the role, biosynthesis, and characteristics of Podophyllotoxin (PTOX) as a potential antitumor agent with particular emphasis on key biosynthesis processes, function of related enzymes and characterization of genes encoding the enzymes.
Materials and methods: Google scholar, PubMed and Scopus were searched for literatures which have studied identification, characterization, fermentation and therapeutic effects of PTOX and published in English language until end of 2016.
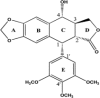
Results: PTOX is an important plant-derived natural product, has derivatives such as etoposide and teniposide, which have been used as therapies for cancers and venereal wart. PTOX structure is closely related to the aryltetralin lactone lignans that have antineoplastic and antiviral activities. Podophyllum emodi Wall. (syn. P. hexandrum) and Podophyllum peltatum L. (Berberidaceae) are the major sources of PTOX. It has been shown that ferulic acid and methylenedioxy substituted cinnamic acid are the enzymes involved in PTOX synthesis. PTOX prevents cell growth via polymerization of tubulin, leading to cell cycle arrest and suppression of the formation of the mitotic-spindles microtubules.
Conclusion: Several investigations have been performed in biosynthesis of PTOX such as cultivation of these plants, though they were unsuccessful. Thus, it is important to find alternative sources to satisfy the pharmaceutical demand for PTOX. Moreover, further preclinical studies are warranted to explore the molecular mechanisms of these agents in treatment of cancer and their possible potential to overcome chemoresistance of tumor cells.
Keywords: Anticancer; Antitumor; Lignans; Natural products; Podophyllotoxin.
Figures
References
-
- Abad AS, López-Pérez JL, Del Olmo E, Garcia-Fernandez LF, Francesch AS, Trigili C, Barasoain I, Andreu JM, Díaz JF, San Feliciano A. Synthesis and antimitotic and tubulin interaction profiles of novel pinacol derivatives of podophyllotoxins. J Med Chem. 2012;55:6724–6737. - PubMed
-
- Aly AH, Debbab A, Kjer J, Proksch P. Fungal endophytes from higher plants: a prolific source of phytochemicals and other bioactive natural products. Fungal Divers. 2010;41:1–16.
-
- Ardalani H, Hassanpour Moghadam M, Rahimi R, Soltani J, Mozayanimonfared A, Moradi M, Azizi A. Sumac as a novel adjunctive treatment in hypertension: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. RSC Adv. 2016;6:11507–11512.
-
- Arican O, Guneri F, Bilgic K, Karaoglu A. Topical Imiquimod 5% Cream in External Anogenital Warts: A Randomized, Double‐Blind, Placebo‐Controlled Study. J Dermatol. 2004;31:627–631. - PubMed
-
- Baldi A, Jain A, Gupta N, Srivastava A, Bisaria V. Co-culture of arbuscular mycorrhiza-like fungi (Piriformospora indica and Sebacina vermifera) with plant cells of Linum album for enhanced production of podophyllotoxins: a first report. Biotechnol Lett. 2008;30:1671–1677. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous