Clinicopathologic and genetic characteristics of young patients with pleural diffuse malignant mesothelioma
- PMID: 28884745
- PMCID: PMC6021688
- DOI: 10.1038/modpathol.2017.108
Clinicopathologic and genetic characteristics of young patients with pleural diffuse malignant mesothelioma
Abstract
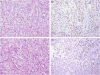
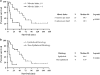
Pleural diffuse malignant mesothelioma typically presents during the seventh decade of life and has poor prognosis. Recent epidemiologic studies have shown differences between young and older mesothelioma patients, but the biology of pleural mesothelioma in young patients is poorly understood. We studied the clinicopathologic and genetic characteristics in pleural mesothelioma patients aged 35 years and younger. Thirty-six consecutive pleural mesothelioma patients aged 35 years and younger were compared with 48 older patients. We examined demographic and clinical characteristics, histologic type, growth patterns, mitotic index, and nuclear grade on hematoxylin and eosin-stained slides, BAP1 protein expression by immunohistochemistry, and CDKN2A and NF2 deletions by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Clinicopathologic and cytogenetic results were compared between young and older groups, and correlated with overall survival. Young patients were more frequently women, reported less asbestos exposure, and had a greater frequency of prior therapeutic radiation and family history of breast cancer than older patients (P<0.05 each). There were no histologic differences between young and older patients (all P>0.05). CDKN2A deletion was less prevalent in young patients (P=0.01), loss of BAP1 protein expression less frequent in young patients (P=0.06), and NF2 deletion rates similar between groups (P>0.05 each). Median overall survival was 40 vs 26 months (P=0.10) in young and older patients, respectively, and 47 vs 31 months (P=0.04) when comparing patients with epithelioid histology only. High mitotic index and non-epithelioid histology were the only characteristics associated with a poor overall survival in young patients. Young patients with pleural mesothelioma have an equal sex distribution and are more likely to have a history of mantle radiation, family history of breast cancer, and lower rates of CDKN2A deletion than older patients. Our results suggest that pleural mesothelioma in young patients has distinctive clinical and genetic characteristics, despite some similarities to pleural mesothelioma in older patients.
Conflict of interest statement
LRC serves on the Advisory board for Merck Sharp & Dohme and undertakes medicolegal work related to mesothelioma and lung cancer. RB receives support from the National Cancer Institute, Verastem, Genentech-Roche, and Castle Biosciences via research grants to Brigham and Women’s Hospital. These financial disclosures do not apply to the current study, which is not associated with a specific source of funding. The remaining author declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Galateau-Salle F, Churg A, Roggli V, et al. Diffuse malignant mesothelioma: epithelioid mesothelioma. In: Travis WD, Brambilla E, Burke AP, et al., editors. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. IARC; Lyon, France: 2015. pp. 156–154.
-
- Neumann V, Günthe S, Mülle KM, et al. Malignant mesothelioma—German mesothelioma register 1987-1999. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2001;74:383–395. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control. Work-Related Lung Disease Surveillance System: Mesothelioma. Available at: http://wwwn.cdc.gov/eworld/Grouping/Malignant_mesothelioma/100 (accessed February 20, 2017)
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

