Fuchs' Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy and RNA Foci in Patients With Myotonic Dystrophy
- PMID: 28886202
- PMCID: PMC5590687
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.17-22350
Fuchs' Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy and RNA Foci in Patients With Myotonic Dystrophy
Abstract
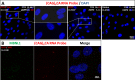
Purpose: The most common cause of Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy (FECD) is an intronic CTG repeat expansion in TCF4. Expanded CUG repeat RNA colocalize with splicing factor, muscleblind-like 1 (MBNL1), in nuclear foci in endothelium as a molecular hallmark. Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) is a neuromuscular disorder caused by a CTG repeat expansion in the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of DMPK. In this study, we examine for RNA-MBNL1 foci in endothelial cells of FECD subjects with DM1, test the hypothesis that DM1 patients are at risk for FECD, and determine prevalence of TCF4 and DMPK expansions in a FECD cohort.
Methods: Using FISH, we examined for nuclear RNA-MBNL1 foci in endothelial cells from FECD subjects with DM1. We examined 13 consecutive unrelated DM1 patients for FECD using slit-lamp and specular microscopy. We genotyped TCF4 and DMPK repeat polymorphisms in a FECD cohort of 317 probands using short-tandem repeat and triplet repeat-primed PCR assays.
Results: We detected abundant nuclear RNA foci colocalizing with MBNL1 in endothelial cells of FECD subjects with DM1. Six of thirteen DM1 patients (46%) had slit-lamp and specular microscopic findings of FECD, compared to 4% disease prevalence (P = 5.5 × 10-6). As expected, 222 out of 317 (70%) FECD probands harbored TCF4 expansion, while one subject harbored DMPK expansion without prior diagnosis of DM1.
Conclusions: Our work suggests that DM1 patients are at risk for FECD. DMPK mutations contribute to the genetic burden of FECD but are uncommon. We establish a connection between two repeat expansion disorders converging upon RNA-MBNL1 foci and FECD.
Figures

Comment in
-
Fuchs' Endothelial and Myotonic Dystrophies: Corneal Dystrophy in Myotonic Patients.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Nov 1;58(13):5838. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-23171. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 29136408 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lorenzetti DW, Uotila MH, Parikh N, Kaufman HE. . Central cornea guttata. Incidence in the general population. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967; 64: 1155– 1158. - PubMed
-
- 2015 Eye Banking Statisical Report. Washington, DC: Eye Bank Association of America; 2016.
-
- Chi HH, Teng CC, Katzin HM. . Histopathology of primary endothelial-epithelial dystrophy of the cornea. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958; 45: 518– 535. - PubMed
-
- Laing RA, Leibowitz HM, Oak SS, Chang R, Berrospi AR, Theodore J. . Endothelial mosaic in Fuchs' dystrophy. A qualitative evaluation with the specular microscope. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981; 99: 80– 83. - PubMed
-
- Bigar F. . Specular microscopy of the corneal endothelium. Optical solutions and clinical results. Dev Ophthalmol. 1982; 6: 1– 94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

