Cost of a measles outbreak in a remote island economy: 2014 Federated States of Micronesia measles outbreak
- PMID: 28886945
- PMCID: PMC5831405
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.08.075
Cost of a measles outbreak in a remote island economy: 2014 Federated States of Micronesia measles outbreak
Abstract
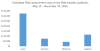
After 20years with no reported measles cases, on May 15, 2014 the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) was notified of two cases testing positive for measles-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies in the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM). Under the Compact of Free Association, FSM receives immunization funding and technical support from the United States (US) domestic vaccination program managed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In a collaborative effort, public health officials and volunteers from FSM and the US government worked to respond and contain the measles outbreak through an emergency mass vaccination campaign, contact tracing, and other outbreak investigation activities. Contributions were also made by United Nations Children's Emergency Fund (UNICEF) and World Health Organization (WHO). Total costs incurred as a result of the outbreak were nearly $4,000,000; approximately $10,000 per case. Direct medical costs (≈$141,000) were incurred in the treatment of those individuals infected, as well as lost productivity of the infected and informal caregivers (≈$250,000) and costs to contain the outbreak (≈$3.5 million). We assessed the economic burden of the 2014 measles outbreak to FSM, as well as the economic responsibilities of the US. Although the US paid the majority of total costs of the outbreak (≈67%), examining each country's costs relative to their respective economy illustrates a far greater burden to FSM. We demonstrate that while FSM was heavily assisted by the US in responding to the 2014 Measles Outbreak, the outbreak significantly impacted their economy. FSM's economic burden from the outbreak is approximately equivalent to their entire 2016 Fiscal Year budget dedicated to education.
Keywords: Cost of outbreak; Economic burden; Federated States of Micronesia; Measles.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have read and approved the manuscript, and there are no financial disclosures, conflicts of interests and/or acknowledgements necessary.
The findings and conclusions in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official position of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Figures

References
-
- McLean HQ, Fiebelkorn AP, Temte JL, Wallace GS Control CfD, Prevention. Prevention of measles, rubella, congenital rubella syndrome, and mumps, 2013: summary recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) MMWR Recomm Rep. 2013;2013(62):1–34. - PubMed
-
- Durrheim DN, Crowcroft NS, Strebel PM. Measles – The epidemiology of elimination. Vaccine. 2014;32:6880–3. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Measles Fact sheet. Avenue Appia 20, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland: 2016.
-
- United States Department of State. U S Relations with the Federated States of Micronesia, Bureau of East Asian and Pacific Affairs Fact Sheet. 2016
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

