Smoking cessation and outcome after ischemic stroke or TIA
- PMID: 28887378
- PMCID: PMC5644463
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004524
Smoking cessation and outcome after ischemic stroke or TIA
Abstract
Objective: To assess whether smoking cessation after an ischemic stroke or TIA improves outcomes compared to continued smoking.
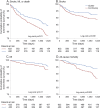
Methods: We conducted a prospective observational cohort study of 3,876 nondiabetic men and women enrolled in the Insulin Resistance Intervention After Stroke (IRIS) trial who were randomized to pioglitazone or placebo within 180 days of a qualifying stroke or TIA and followed up for a median of 4.8 years. A tobacco use history was obtained at baseline and updated during annual interviews. The primary outcome, which was not prespecified in the IRIS protocol, was recurrent stroke, myocardial infarction (MI), or death. Cox regression models were used to assess the differences in stroke, MI, and death after 4.8 years, with correction for adjustment variables prespecified in the IRIS trial: age, sex, stroke (vs TIA) as index event, history of stroke, history of hypertension, history of coronary artery disease, and systolic and diastolic blood pressures.
Results: At the time of their index event, 1,072 (28%) patients were current smokers. By the time of randomization, 450 (42%) patients had quit smoking. Among quitters, the 5-year risk of stroke, MI, or death was 15.7% compared to 22.6% for patients who continued to smoke (adjusted hazard ratio 0.66, 95% confidence interval 0.48-0.90).
Conclusion: Cessation of cigarette smoking after an ischemic stroke or TIA was associated with significant health benefits over 4.8 years in the IRIS trial cohort.
© 2017 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Reader response: Smoking cessation and outcome after ischemic stroke or TIA.Neurology. 2018 Jun 5;90(23):1082. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000005631. Neurology. 2018. PMID: 29866936 No abstract available.
-
Rauchstopp verhindert Apoplex-Rezidive.MMW Fortschr Med. 2018 Sep;160(15):41. doi: 10.1007/s15006-018-0883-4. MMW Fortschr Med. 2018. PMID: 30206851 German. No abstract available.
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics–2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016;133:e38–e360. - PubMed
-
- O'Donnell MJ, Chin SL, Rangarajan S, et al. Global and regional effects of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with acute stroke in 32 countries (INTERSTROKE): a case-control study. Lancet 2016;388:761–775. - PubMed
-
- Jamal A, King BA, Neff LJ, Whitmill J, Babb SD, Graffunder CM. Current cigarette smoking among adults—United States, 2005–2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2016;65:1205–1211. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical