Comparison of three multiplex gastrointestinal platforms for the detection of gastroenteritis viruses
- PMID: 28889082
- PMCID: PMC5940486
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2017.08.012
Comparison of three multiplex gastrointestinal platforms for the detection of gastroenteritis viruses
Abstract
Background: Viruses are major etiological agents of childhood gastroenteritis. In recent years, several molecular platforms for the detection of viral enteric pathogens have become available.
Objective/study design: We evaluated the performance of three multiplex platforms including Biofire's Gastrointestinal Panel (FilmArray), Luminex xTAG® Gastrointestinal Pathogen Panel (GPP), and the TaqMan Array Card (TAC) for the detection of five gastroenteritis viruses using a coded panel of 300 archived stool samples.
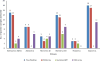
Results: The FilmArray detected a virus in 199 (96.1%) and the TAC in 172 (83.1%) of the 207 samples (187 samples positive for a single virus and 20 samples positive for more than one virus) whereas the GPP detected a virus in 100 (78.7%) of the 127 (97 positive for one virus and three positive for more than one virus) samples. Overall the clinical accuracy was highest for the FilmArray (98%) followed by TAC (97.2%) and GPP (96.9%). The sensitivity of the FilmArray, GPP and TAC platforms was highest for rotavirus (100%, 95.8%, and 89.6%, respectively) and lowest for adenovirus type 40/41 (97.4%, 57.9% and 68.4%). The specificity of the three platforms ranged from 95.6% (rotavirus) to 99.6% (norovirus/sapovirus) for the FilmArray, 99.6% (norovirus) to 100% (rotavirus/adenovirus) for GPP, and 98.9% (astrovirus) to 100% (rotavirus/sapovirus) for TAC.
Conclusion: The FilmArray demonstrated the best analytical performance followed by TAC. In recent years, the availability of multi-enteric molecular testing platforms has increased significantly and our data highlight the strengths and weaknesses of these platforms.
Keywords: Adenovirus type 40/41; Astrovirus; Gastroenteritis viruses; Norovirus; Rotavirus; Sapovirus.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
James Chappell has served as a consultant to Luminex Molecular Diagnostics on the xTAG Gastrointestinal Pathogen Panel (GPP) and received research support from Luminex to perform GPP analysis of specimens collected through the CDC New Vaccine Surveillance Network. Additionally, he collaborates with Luminex evaluating new technology for the diagnosis of
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Farthing M, Salam MA, Lindberg G, Dite P, Khalif I, Salazar-Lindo E, et al. Acute diarrhea in adults and children: a global perspective. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2013;47:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Chhabra P, Payne DC, Szilagyi PG, Edwards KM, Staat MA, Shirley SH, et al. Etiology of viral gastroenteritis in children < 5 years of age in the United States, 2008–2009. J Infect Dis. 2013;208:790–800. - PubMed
-
- Staat MA, Payne DC, Donauer S, Weinberg GA, Edwards KM, Szilagyi PG, et al. Effectiveness of pentavalent rotavirus vaccine against severe disease. Pediatrics. 2011;128:e267–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

