Anti-carbamylated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis patients and their association with rheumatoid factor
- PMID: 28889152
- PMCID: PMC5654028
- DOI: 10.15537/smj.2017.9.20841
Anti-carbamylated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis patients and their association with rheumatoid factor
Abstract
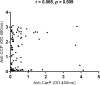
To evaluate levels of anti-carbamylated protein (anti-CarP) antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and to determine their association with serological parameters and disease activity. Methods: A cross-sectional study involving 105 multiethnic RA patients (48 rheumatoid factor [RF]-positive and 57 RF-negative patients) was conducted at Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia, Kelantan, Malaysia, from January 2015 to February 2016. Fifty healthy controls (HCs) were included. C-reactive protein (CRP), RF, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) and anti-CarP antibodies were measured. A health assessment questionnaire (HAQ) was administered to the study participants and 28-joint Disease Activity Score (DAS28) were obtained. Results: The level of anti-CarP antibodies was significantly increased in the RA patients compared with HCs (p=0.042). The presence of anti-CarP antibodies was significantly associated with RF (p=0.019) and the HAQ (p=0.010). A significant association between the presence of anti-CarP antibodies and the DAS28 was not found (p=0.632). Conclusion: Our study provides further evidence that the level of anti-CarP antibodies is significantly elevated in RA patients.
Figures
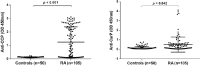
References
-
- Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2010;376:1094–108. - PubMed
-
- Verheul M, Fearon U, Trouw L, Veale D. Biomarkers for rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Immunol. 2015;161:2–10. - PubMed
-
- Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D, Carmona L, Wolfe F, Vos T, et al. The global burden of rheumatoid arthritis: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:1316–1322. - PubMed
-
- Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2569–2581. - PubMed
-
- Jaskowski TD, Hill HR, Russo KL, Lakos G, Szekanecz Z, Teodorescu M. Relationship between rheumatoid factor isotypes and IgG anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies. J Rheumatol. 2010;37:1582–1588. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

