Overall Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma
- PMID: 28889792
- PMCID: PMC5706778
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1709684
Overall Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma
Erratum in
-
Neoadjuvant PD-1 Blockade in Resectable Lung Cancer; Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma; Overall Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma; Prolonged Survival in Stage III Melanoma with Ipilimumab Adjuvant Therapy; Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab or Monotherapy in Untreated Melanoma; Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab or Monotherapy in Untreated Melanoma; Nivolumab and Ipilimumab versus Ipilimumab in Untreated Melanoma; Rapid Eradication of a Bulky Melanoma Mass with One Dose of Immunotherapy; Genetic Basis for Clinical Response to CTLA-4 Blockade; Genetic Basis for Clinical Response to CTLA-4 Blockade in Melanoma; Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma; Safety and Tumor Responses with Lambrolizumab (Anti-PD-1) in Melanoma; Hepatotoxicity with Combination of Vemurafenib and Ipilimumab.N Engl J Med. 2018 Nov 29;379(22):2185. doi: 10.1056/NEJMx180040. Epub 2018 Nov 9. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 31442371 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Nivolumab combined with ipilimumab resulted in longer progression-free survival and a higher objective response rate than ipilimumab alone in a phase 3 trial involving patients with advanced melanoma. We now report 3-year overall survival outcomes in this trial.
Methods: We randomly assigned, in a 1:1:1 ratio, patients with previously untreated advanced melanoma to receive nivolumab at a dose of 1 mg per kilogram of body weight plus ipilimumab at a dose of 3 mg per kilogram every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by nivolumab at a dose of 3 mg per kilogram every 2 weeks; nivolumab at a dose of 3 mg per kilogram every 2 weeks plus placebo; or ipilimumab at a dose of 3 mg per kilogram every 3 weeks for four doses plus placebo, until progression, the occurrence of unacceptable toxic effects, or withdrawal of consent. Randomization was stratified according to programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) status, BRAF mutation status, and metastasis stage. The two primary end points were progression-free survival and overall survival in the nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group and in the nivolumab group versus the ipilimumab group.
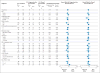
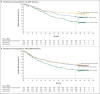
Results: At a minimum follow-up of 36 months, the median overall survival had not been reached in the nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group and was 37.6 months in the nivolumab group, as compared with 19.9 months in the ipilimumab group (hazard ratio for death with nivolumab plus ipilimumab vs. ipilimumab, 0.55 [P<0.001]; hazard ratio for death with nivolumab vs. ipilimumab, 0.65 [P<0.001]). The overall survival rate at 3 years was 58% in the nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group and 52% in the nivolumab group, as compared with 34% in the ipilimumab group. The safety profile was unchanged from the initial report. Treatment-related adverse events of grade 3 or 4 occurred in 59% of the patients in the nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group, in 21% of those in the nivolumab group, and in 28% of those in the ipilimumab group.
Conclusions: Among patients with advanced melanoma, significantly longer overall survival occurred with combination therapy with nivolumab plus ipilimumab or with nivolumab alone than with ipilimumab alone. (Funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb and others; CheckMate 067 ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01844505 .).
Figures

Comment in
-
Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma.N Engl J Med. 2017 Dec 21;377(25):2503. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1714339. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 29265785 No abstract available.
-
Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma.N Engl J Med. 2017 Dec 21;377(25):2503. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1714339. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 29265786 No abstract available.
-
First report of overall survival for ipilimumab plus nivolumab from the phase III Checkmate 067 study in advanced melanoma.Ann Oncol. 2018 Mar 1;29(3):542-543. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy020. Ann Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29360923 No abstract available.
-
A new era of proactive melanoma therapy: hit hard, hit early.Br J Dermatol. 2018 Apr;178(4):817-820. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16347. Br J Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29668089 No abstract available.
-
Nivolumab versus ipilimumab in the treatment of advanced melanoma: a critical appraisal: ORIGINAL ARTICLE: Wolchok JD, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R et al. Overall survival with combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med 2017; 377:1345-56.Br J Dermatol. 2018 Aug;179(2):296-300. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16785. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Br J Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29766492
-
Immunotherapy Combinations Proliferating in Immuno-Oncology.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021 Nov 29;113(12):1787-1788. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djx284. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021. PMID: 36394225 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
