An experimental study of executive function and social impairment in Cornelia de Lange syndrome
- PMID: 28889797
- PMCID: PMC5592717
- DOI: 10.1186/s11689-017-9213-x
An experimental study of executive function and social impairment in Cornelia de Lange syndrome
Abstract
Background: Extreme shyness and social anxiety is reported to be characteristic of adolescents and adults with Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS); however, the nature of these characteristics is not well documented. In this study, we develop and apply an experimental assessment of social anxiety in a group of adolescents and adults with CdLS to determine the nature of the social difficulties and whether they are related to impairments in executive functioning.
Methods: A familiar and unfamiliar examiner separately engaged in socially demanding tasks comprising three experimental conditions with a group of individuals with CdLS (n = 25; % male = 44; mean age = 22.16; SD = 8.81) and a comparable group of individuals with Down syndrome (DS; n = 20; % male = 35; mean age = 24.35; SD = 5.97). Behaviours indicative of social anxiety were coded. The Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function-Preschool version, an informant measure of executive function, was completed by participants' caregivers.
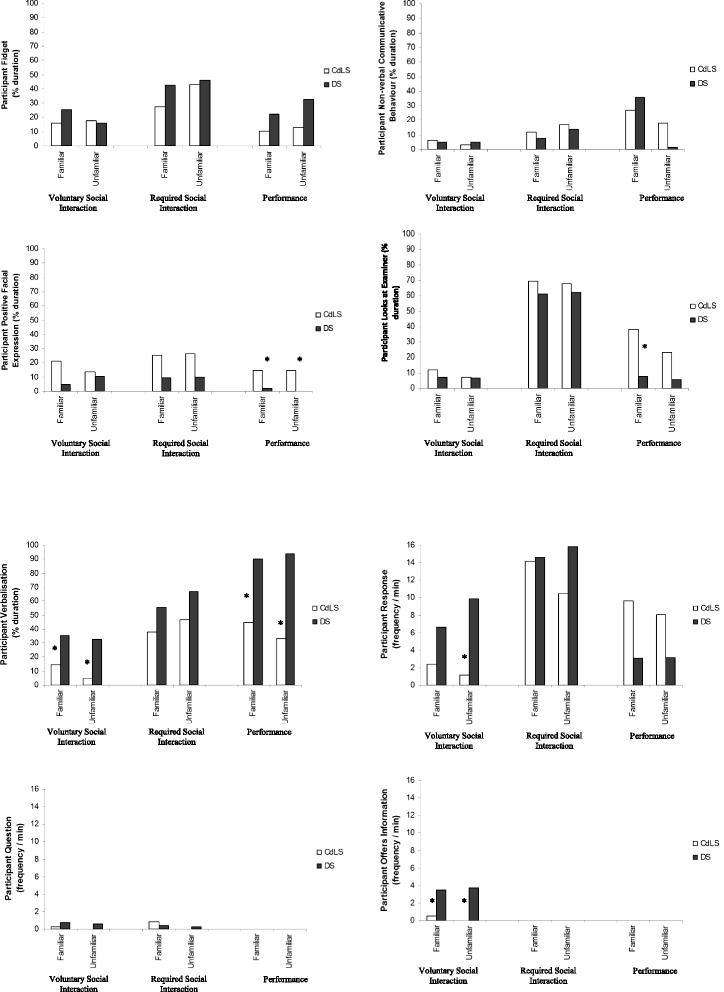
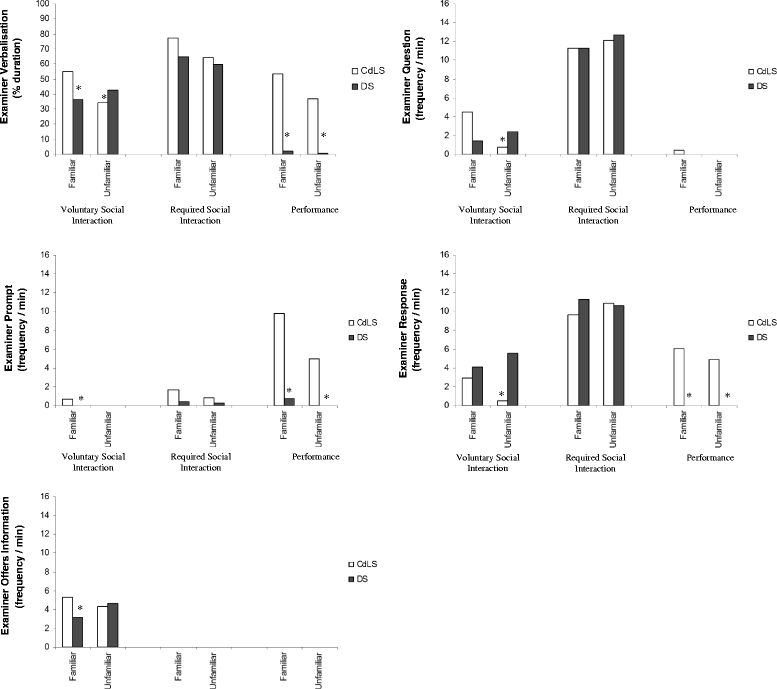
Results: Significantly less verbalisation was observed in the CdLS group than the DS group in conditions requiring the initiation of speech. In the CdLS group, impairments in verbalisation were not associated with a greater degree of intellectual disability but were significantly correlated with impairments in both planning and working memory. This association was not evident in the DS group.
Conclusions: Adolescents and adults with CdLS have a specific difficulty with the initiation of speech when social demands are placed upon them. This impairment in verbalisation may be underpinned by specific cognitive deficits, although further research is needed to investigate this fully.
Keywords: Cornelia de Lange syndrome; Down syndrome; Executive function; Social anxiety.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval for the current study was obtained from the School of Psychology Ethical Review Board at the University of Birmingham. Participants aged 16 and above provided written consent to participate. Parents of children aged below 16 years provided written consent on behalf of their children.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Behavioural and psychological characteristics in Pitt-Hopkins syndrome: a comparison with Angelman and Cornelia de Lange syndromes.J Neurodev Disord. 2019 Oct 5;11(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s11689-019-9282-0. J Neurodev Disord. 2019. PMID: 31586495 Free PMC article.
-
Executive functioning in Cornelia de Lange syndrome: domain asynchrony and age-related performance.J Neurodev Disord. 2017 Aug 15;9(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s11689-017-9208-7. J Neurodev Disord. 2017. PMID: 28806899 Free PMC article.
-
Low speech rate but high gesture rate during conversational interaction in people with Cornelia de Lange syndrome.J Intellect Disabil Res. 2021 Jun;65(6):601-607. doi: 10.1111/jir.12829. Epub 2021 Mar 10. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2021. PMID: 33694205
-
Exome sequencing identifies a novel EP300 frame shift mutation in a patient with features that overlap Cornelia de Lange syndrome.Am J Med Genet A. 2014 Jan;164A(1):251-8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36237. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Am J Med Genet A. 2014. PMID: 24352918 Review.
-
Behavioral and psychiatric manifestations in Cornelia de Lange syndrome.Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2017 Mar;30(2):92-96. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000311. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28125439 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Behavioural Assessment of Social Anxiety and Social Motivation in Fragile X, Cornelia de Lange and Rubinstein-Taybi Syndromes.J Autism Dev Disord. 2020 Jan;50(1):127-144. doi: 10.1007/s10803-019-04232-5. J Autism Dev Disord. 2020. PMID: 31541420
-
An Observational Study of Social Interaction Skills and Behaviors in Cornelia de Lange, Fragile X and Rubinstein-Taybi Syndromes.J Autism Dev Disord. 2020 Nov;50(11):4001-4010. doi: 10.1007/s10803-020-04440-4. J Autism Dev Disord. 2020. PMID: 32189229 Free PMC article.
-
The developmental trajectories of the behavioral phenotype and neuropsychiatric functioning in Cornelia de Lange and Rubinstein Taybi syndromes: A longitudinal study.Am J Med Genet A. 2023 Feb;191(2):424-436. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.63039. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Am J Med Genet A. 2023. PMID: 36373849 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioural and psychological characteristics in Pitt-Hopkins syndrome: a comparison with Angelman and Cornelia de Lange syndromes.J Neurodev Disord. 2019 Oct 5;11(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s11689-019-9282-0. J Neurodev Disord. 2019. PMID: 31586495 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

