Horizontally Acquired Genes Are Often Shared between Closely Related Bacterial Species
- PMID: 28890711
- PMCID: PMC5575156
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01536
Horizontally Acquired Genes Are Often Shared between Closely Related Bacterial Species
Abstract
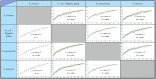
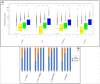
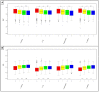
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) serves as an important source of innovation for bacterial species. We used a pangenome-based approach to identify genes that were horizontally acquired by four closely related bacterial species, belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family. This enabled us to examine the extent to which such closely related species tend to share horizontally acquired genes. We find that a high percent of horizontally acquired genes are shared among these closely related species. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the extent of sharing of horizontally acquired genes among these four closely related species is predictive of the extent to which these genes will be found in additional bacterial species. Finally, we show that acquired genes shared by more species tend to be better optimized for expression within the genomes of their new hosts. Combined, our results demonstrate the existence of a large pool of frequently horizontally acquired genes that have distinct characteristics from horizontally acquired genes that are less frequently shared between species.
Keywords: bacterial evolution; gene content; genome composition; horizontal gene transfer; pangenome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detecting Horizontal Gene Transfer between Closely Related Taxa.PLoS Comput Biol. 2015 Oct 6;11(10):e1004408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004408. eCollection 2015 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015. PMID: 26439115 Free PMC article.
-
Speciation in Chlamydia: genomewide phylogenetic analyses identified a reliable set of acquired genes.J Mol Evol. 2003 Dec;57(6):672-80. doi: 10.1007/s00239-003-2517-3. J Mol Evol. 2003. PMID: 14745536
-
Effect of the environment on horizontal gene transfer between bacteria and archaea.PeerJ. 2017 Sep 29;5:e3865. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3865. eCollection 2017. PeerJ. 2017. PMID: 28975058 Free PMC article.
-
Horizontal gene transfer, genome innovation and evolution.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005 Sep;3(9):679-87. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1204. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16138096 Review.
-
Horizontal gene transfer in cyanobacterial signature genes.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;532:339-66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-853-9_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19271195 Review.
Cited by
-
PPanGGOLiN: Depicting microbial diversity via a partitioned pangenome graph.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Mar 19;16(3):e1007732. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007732. eCollection 2020 Mar. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32191703 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic insights and metabolic profiling of gut commensal Luoshenia tenuis at strain level.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2025 Aug 5;11(1):153. doi: 10.1038/s41522-025-00793-9. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2025. PMID: 40764512 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of antimicrobial resistance related genes in E. coli, Salmonella and Klebsiella isolates from broilers in the West Region of Cameroon.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 11;18(1):e0280150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280150. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36630464 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics reveals genetic diversity and differential metabolic potentials of the species of Arachnia and suggests reclassification of Arachnia propionica E10012 (=NBRC_14587) as novel species.Arch Microbiol. 2025 Mar 18;207(4):93. doi: 10.1007/s00203-025-04302-6. Arch Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40100361
-
Phylogenomic disentangling of the Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis taxon.Microb Genom. 2021 Jul;7(7):000609. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000609. Microb Genom. 2021. PMID: 34319225 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

