Musical Training Enhances Neural Processing of Comodulation Masking Release in the Auditory Brainstem
- PMID: 28890775
- PMCID: PMC5582414
- DOI: 10.4081/audiores.2017.185
Musical Training Enhances Neural Processing of Comodulation Masking Release in the Auditory Brainstem
Abstract
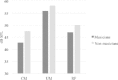
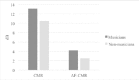
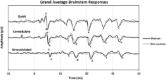
Musical training strengthens segregation the target signal from background noise. Musicians have enhanced stream segregation, which can be considered a process similar to comodulation masking release. In the current study, we surveyed psychoacoustical comodulation masking release in musicians and non-musicians. We then recorded the brainstem responses to complex stimuli in comodulated and unmodulated maskers to investigate the effect of musical training on the neural representation of comodulation masking release for the first time. The musicians showed significantly greater amplitudes and earlier brainstem response timing for stimulus in the presence of comodulated maskers than non-musicians. In agreement with the results of psychoacoustical experiment, musicians showed greater comodulation masking release than non-musicians. These results reveal a physiological explanation for behavioral enhancement of comodulation masking release and stream segregation in musicians.
Keywords: Musical training; auditory brainstem response; comodulation masking release.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brainstem Correlates of Comodulation Masking Release for Speech in Normal Hearing Adults.J Audiol Otol. 2018 Jul;22(3):128-133. doi: 10.7874/jao.2017.00283. Epub 2018 Apr 17. J Audiol Otol. 2018. PMID: 29656636 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical representation of release from auditory masking.Neuroimage. 2010 Jan 1;49(1):835-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.07.014. Epub 2009 Jul 17. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 19616635
-
Comodulation masking release in the inferior colliculus by combined signal enhancement and masker reduction.J Neurophysiol. 2017 Feb;117(2):853-867. doi: 10.1152/jn.00191.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 26. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 27784801 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation discrimination interference and comodulation masking release as a function of the number and spectral placement of narrow-band noise modulators.J Acoust Soc Am. 1996 Oct;100(4 Pt 1):2373-81. doi: 10.1121/1.417947. J Acoust Soc Am. 1996. PMID: 8865644
-
The psychophysics and physiology of comodulation masking release.Exp Brain Res. 2003 Dec;153(4):405-17. doi: 10.1007/s00221-003-1607-1. Epub 2003 Sep 9. Exp Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 13680049 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurophysiological improvements in speech-in-noise task after short-term choir training in older adults.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Apr 6;13(7):9468-9495. doi: 10.18632/aging.202931. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33824226 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric Flankers in Comodulation Masking Release.J Audiol Otol. 2019 Jan;23(1):27-32. doi: 10.7874/jao.2018.00192. Epub 2018 Aug 22. J Audiol Otol. 2019. PMID: 30126261 Free PMC article.
-
Brainstem Correlates of Comodulation Masking Release for Speech in Normal Hearing Adults.J Audiol Otol. 2018 Jul;22(3):128-133. doi: 10.7874/jao.2017.00283. Epub 2018 Apr 17. J Audiol Otol. 2018. PMID: 29656636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ericsson KA, Krampe RT, Tesch-romer C, et al. The role of deliberate practice in the acquisition of expert performance. BMC Med Educ 1993;100:363-406.
-
- Micheyl C, Delhommeau K, Perrot X, Oxenham AJ. Influence of musical and psychoacoustical training on pitch discrimination. Proc Meet Acoust 2006;219:36-47. - PubMed
-
- Strait D, Skoe E, Kraus N, Ashley R. Musical experience influences subcortical processing of emotionally-salient vocal sounds. Eur J Neurosci 2009;29:661-8. - PubMed
-
- Peretz I, Zatorre RJ. Brain organization for music processing. Annu Rev Psychol 2005;56:89-114. - PubMed
-
- Hall JW, Haggard MP, Fernandes MA. Detection in noise by spectro-temporal pattern analysis. J Acoust Soc Am 1984;76:50-56. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
