Circulating miR-92a, miR-143 and miR-342 in Plasma are Novel Potential Biomarkers for Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 28890884
- PMCID: PMC5581549
- DOI: 10.22088/acadpub.BUMS.6.2.2
Circulating miR-92a, miR-143 and miR-342 in Plasma are Novel Potential Biomarkers for Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
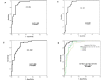
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that function as post-transcriptional gene expression regulators. The expression profiling of miRNAs has already entered into cancer clinics as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers to assess tumor initiation, progression and response to treatment in cancer patients. Recent studies have opened the way for the use of circulating miRNAs as non-invasive diagnosis and prognosis of Acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The aim of this study was to identify plasma miR-92a, miR-143 and miR-342 expression signatures in AML patients to introduce new markers for establishing AML diagnosis and prognosis. Blood samples were collected from 65 AML patients and 50 controls. The expression of three target miRNAs (miR-92a, miR-143 and miR-342) was measured using quantitative real-time PCR method. Plasma levels of miR-92a, miR-143 and miR-342 were significantly lower in AML patients in comparison with control group. Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) analysis revealed that the sensitivity and specificity values of miR-92a were 81.5% and 94%, respectively, with a cut-off value of 0.704. The sensitivity and specificity values of miR-143 were 87.7% and 80%, respectively, with a cut-off value of 0.65. The sensitivity and specificity values of miR-342 were 75.4% and 90%, respectively, with a cut-off value of 0.479. Our findings suggest that plasma miR-92a, miR-143 and miR-342 could be promising novel circulating biomarkers in clinical detection of AML.
Keywords: Leukemia; acute; diagnosis; microRNAs; myeloid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Khasawneh MK, Abdel-Wahab O. Recent discoveries in molecular characterization of acute myeloid leukemia. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2014;9:93–9. - PubMed
-
- Foran JM. New prognostic markers in acute myeloid leukemia: perspective from the clinic. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2010;2010:47–55. - PubMed
-
- Estey EH. Acute myeloid leukemia: 2013 update on risk-stratification and management. Am J Hematol. 2013;88:318–27. - PubMed
-
- Thol F, Ganser A. Molecular pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia: a diverse disease with new perspectives. Front Med China. 2010;4:356–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
