Epigenetics and Immunometabolism in Diabetes and Aging
- PMID: 28891325
- PMCID: PMC6012980
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2017.7299
Epigenetics and Immunometabolism in Diabetes and Aging
Abstract
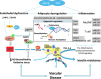
Significance: A strong relationship between hyperglycemia, impaired insulin pathway, and cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes (T2D) is linked to oxidative stress and inflammation. Immunometabolic pathways link these pathogenic processes and pose important potential therapeutic targets. Recent Advances: The link between immunity and metabolism is bidirectional and includes the role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of metabolic disorders such as T2D, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and hypertension and the role of metabolic factors in regulation of immune cell functions. Low-grade inflammation, oxidative stress, balance between superoxide and nitric oxide, and the infiltration of macrophages, T cells, and B cells in insulin-sensitive tissues lead to metabolic impairment and accelerated aging.
Critical issues: Inflammatory infiltrate and altered immune cell phenotype precede development of metabolic disorders. Inflammatory changes are tightly linked to alterations in metabolic status and energy expenditure and are controlled by epigenetic mechanisms.
Future directions: A better comprehension of these mechanistic insights is of utmost importance to identify novel molecular targets. In this study, we describe a complex scenario of epigenetic changes and immunometabolism linking to diabetes and aging-associated vascular disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 29, 257-274.
Keywords: diabetes; epigenetics; inflammation; nitric oxide; superoxide; vascular.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- 2017 IDF. Global Burden: Prevalence and Projections, 2015 and 2040. 2017. www.diabetesatlas.org/across-the-globe.html (accessed April24, 2017)
-
- Abu-Farha M, Tiss A, Abubaker J, Khadir A, Al-Ghimlas F, Al-Khairi I, Baturcam E, Cherian P, Elkum N, Hammad M, John J, Kavalakatt S, Warsame S, Behbehani K, Dermime S, and Dehbi M. Proteomics analysis of human obesity reveals the epigenetic factor HDAC4 as a potential target for obesity. PLoS One 8: e75342, 2013 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alcendor RR, Gao S, Zhai P, Zablocki D, Holle E, Yu X, Tian B, Wagner T, Vatner SF, and Sadoshima J. Sirt1 regulates aging and resistance to oxidative stress in the heart. Circ Res 100: 1512–1521, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Alexander JS. and Becker F. Dual signals underlying diabetic lymphatic barrier dysregulation. Cardiovasc Res 107: 3–4, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Almeida L, Lochner M, Berod L, and Sparwasser T. Metabolic pathways in T cell activation and lineage differentiation. Semin Immunol 28: 514–524, 2016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

