The PI3Kδ Inhibitor Idelalisib Inhibits Homing in an in Vitro and in Vivo Model of B ALL
- PMID: 28891959
- PMCID: PMC5615336
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers9090121
The PI3Kδ Inhibitor Idelalisib Inhibits Homing in an in Vitro and in Vivo Model of B ALL
Abstract
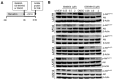
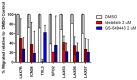
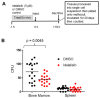
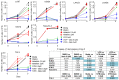
The quest continues for targeted therapies to reduce the morbidity of chemotherapy and to improve the response of resistant leukemia. Adhesion of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells to bone marrow stromal cells triggers intracellular signals that promote cell-adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR). Idelalisib, an U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved PI3Kδ-specific inhibitor has been shown to be effective in CLL in down-regulating p-Akt and prolonging survival in combination with Rituximab; herein we explore the possibility of its use in B ALL and probe the mechanism of action. Primary B ALL in contact with OP9 stromal cells showed increased p-Aktser473. Idelalisib decreased p-Akt in patient samples of ALL with diverse genetic lesions. Addition of idelalisib to vincristine inhibited proliferation when compared to vincristine monotherapy in a subset of samples tested. Idelalisib inhibited ALL migration to SDF-1α in vitro and blocked homing of ALL cells to the bone marrow in vivo. This report tests PI3Kδ inhibitors in a more diverse group of ALL than has been previously reported and is the first published report of idelalisib inhibiting homing of ALL cells to bone marrow. Our data support further pre-clinical evaluation of idelalisib for the therapy of B ALL.
Keywords: ALL; CAM-DR; PI3K; drug resistance; idelalisib; leukemia; migration; mouse model.
Conflict of interest statement
Gilead Sciences provided the drugs and some funding for this research; aside from that the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hunger S.P., Lu X., Devidas M., Camitta B.M., Gaynon P.S., Winick N.J., Reaman G.H., Carroll W.L. Improved survival for children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia between 1990 and 2005: A report from the children’s oncology group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012;30:1663–1669. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.37.8018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chantry D., Vojtek A., Kashishian A., Holtzman D.A., Wood C., Gray P.W., Cooper J.A., Hoekstra M.F. P110delta, a novel phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit that associates with p85 and is expressed predominantly in leukocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:19236–19241. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.31.19236. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

