State of Panax ginseng Research: A Global Analysis
- PMID: 28892002
- PMCID: PMC6151615
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22091518
State of Panax ginseng Research: A Global Analysis
Abstract
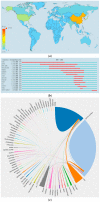
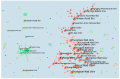
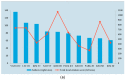
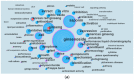
This article aims to understand the global and longitudinal trends of research on Panax ginseng. We used bibliometrics to analyze 3974 papers collected from the Web of ScienceTM Core Collection database during 1959-2016. The number of publications showed a steady growth before 2000 and exponentially increased in stage III (2000-2016, about 86% of the papers were published). Research on P. ginseng was conducted in 64 countries, mainly in Asia; in particular, 41% and 28% of the publications were from South Korea and China, respectively. The institutions from South Korea and China had high publication output and close cooperation and provided the majority of financial support. All top 10 authors and four of the top 20 journals in terms of number of publications originated from South Korea. The leading research subjects were pharmacology (39%), plant science (26%), and integrative complementary medicine (19%). The hotspot of P. ginseng research transformed from basic science to application, and multidisciplinary sciences will play a substantial role in the future. This study provides a comprehensive analysis to elucidate the global distribution, collaboration patterns, and research trends in the P. ginseng domain.
Keywords: Panax ginseng; bibliometrics; emerging trends; global cooperation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Unlu A., Nayir E., Kirca O., Ay H., Ozdogan M. Ginseng and cancer. J. Buon. 2016;21:1383–1387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

