A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies 17 new Parkinson's disease risk loci
- PMID: 28892059
- PMCID: PMC5812477
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3955
A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies 17 new Parkinson's disease risk loci
Abstract
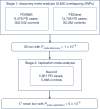
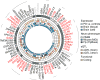
Common variant genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have, to date, identified >24 risk loci for Parkinson's disease (PD). To discover additional loci, we carried out a GWAS comparing 6,476 PD cases with 302,042 controls, followed by a meta-analysis with a recent study of over 13,000 PD cases and 95,000 controls at 9,830 overlapping variants. We then tested 35 loci (P < 1 × 10-6) in a replication cohort of 5,851 cases and 5,866 controls. We identified 17 novel risk loci (P < 5 × 10-8) in a joint analysis of 26,035 cases and 403,190 controls. We used a neurocentric strategy to assign candidate risk genes to the loci. We identified protein-altering or cis-expression quantitative trait locus (cis-eQTL) variants in linkage disequilibrium with the index variant in 29 of the 41 PD loci. These results indicate a key role for autophagy and lysosomal biology in PD risk, and suggest potential new drug targets for PD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: details are available in the
Figures
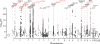
Comment in
-
Novel Parkinson's disease risk loci identified through a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies.Mov Disord. 2018 Jan;33(1):74. doi: 10.1002/mds.27276. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Mov Disord. 2018. PMID: 29266412 No abstract available.
References
-
- Corti O, Lesage S, Brice A. What genetics tells us about the causes and mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease. Physiol. Rev. 2011;91:1161–1218. - PubMed
-
- Verstraeten A, Theuns J, Van Broeckhoven C. Progress in unraveling the genetic etiology of Parkinson disease in a genomic era. Trends Genet. 2015;31:140–149. - PubMed
-
- Nussbaum RL, Ellis CE. Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1356–1364. - PubMed
-
- Shulman JM, De Jager PL, Feany MB. Parkinson’s disease: genetics and pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011;6:193–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

