Effects of vagus nerve stimulation on extinction of conditioned fear and post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms in rats
- PMID: 28892066
- PMCID: PMC5611754
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2017.191
Effects of vagus nerve stimulation on extinction of conditioned fear and post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms in rats
Abstract
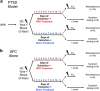
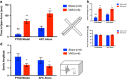
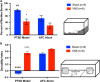
Exposure-based therapies help patients with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) to extinguish conditioned fear of trauma reminders. However, controlled laboratory studies indicate that PTSD patients do not extinguish conditioned fear as well as healthy controls, and exposure therapy has high failure and dropout rates. The present study examined whether vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) augments extinction of conditioned fear and attenuates PTSD-like symptoms in an animal model of PTSD. To model PTSD, rats were subjected to a single prolonged stress (SPS) protocol, which consisted of restraint, forced swim, loss of consciousness, and 1 week of social isolation. Like PTSD patients, rats subjected to SPS show impaired extinction of conditioned fear. The SPS procedure was followed, 1 week later, by auditory fear conditioning (AFC) and extinction. VNS or sham stimulation was administered during half of the extinction days, and was paired with presentations of the conditioned stimulus. One week after completion of extinction training, rats were given a battery of behavioral tests to assess anxiety, arousal and avoidance. Results indicated that rats given SPS 1 week prior to AFC (PTSD model) failed to extinguish the freezing response after eleven consecutive days of extinction. Administration of VNS reversed the extinction impairment and attenuated reinstatement of the conditioned fear response. Delivery of VNS during extinction also eliminated the PTSD-like symptoms, such as anxiety, hyperarousal and social avoidance for more than 1 week after VNS treatment. These results provide evidence that extinction paired with VNS treatment can lead to remission of fear and improvements in PTSD-like symptoms. Taken together, these findings suggest that VNS may be an effective adjunct to exposure therapy for the treatment of PTSD.
Conflict of interest statement
RLR is an owner of Vulintis Inc. and Optokinetics. RLR is a consultant for Konan Medical USA. None of these financial interests are related to this work. MPK is a paid consultant for and shareholder of MicroTransponder. MPK and CKM are authors of a patent entitled ‘Enhancing Fear Extinction using Vagus Nerve Stimulation’. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- American Psychiatric AssociationDiagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.5th edn, American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013.
-
- Maercker A, Michael T, Fehm L, Becker ES, Margraf J. Age of traumatisation as a predictor of post-traumatic stress disorder or major depression in young women. Br J Psychiatry 2004; 184: 482–487. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

