Elevated expression of ΔNp63 in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 28892579
- PMCID: PMC5666030
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13394
Elevated expression of ΔNp63 in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
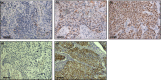
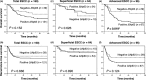
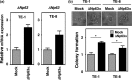
This study aims to explore the expression level of ΔNp63 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). To investigate the association between ΔNp63 (p40) expression and ESCC biology, we compared the levels of ΔNp63 expression in normal and tumor tissues, with a specific focus on the diagnostic value of ΔNp63 in ESCC. We analyzed 160 consecutive patients with ESCC who underwent surgical resection without neoadjuvant chemotherapy at Gunma University Hospital (Maebashi, Japan) between September 2000 and January 2010. The clinicopathological characteristics and survival of patients were subclassified based on the expression of ΔNp63 as determined by immunohistochemistry, indicating that ΔNp63 was highly expressed in 75.6% (121/160) of ESCC patients. Clinicopathological analysis of ΔNp63 expression showed that ΔNp63-positive tumors significantly correlated with two important clinical parameters: T factor (P = 0.0316) and venous invasion (P = 0.0195). The 5-year overall survival rates of advanced ESCC patients with positive and negative expression of ΔNp63 were 35.6% and 71.7%, respectively. Multivariate analysis revealed that the expression of ΔNp63 was identified as an independent prognostic factor (P = 0.0049) in advanced ESCC. In line with this, ΔNp63α-transduced ESCC cell lines increased tumor growth in a soft agar colony formation assay. We report here for the first time that ΔNp63 expression increases the oncogenic potential of ESCC and is an independent marker for predicting poor outcome in advanced ESCC. Our findings suggest that ΔNp63 could serve as a new diagnostic marker for ESCC and might be a relevant therapeutic target for the treatment of patients with this disease.
Keywords: Carcinogenesis; TP63; esophageal cancer; squamous cell carcinoma; ΔNp63/p40.
© 2017 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
References
-
- Kuwano H, Kato H, Miyazaki T et al Genetic alterations in esophageal cancer. Surg Today 2005; 35: 7–18. - PubMed
-
- Melino G, Lu X, Gasco M, Crook T, Knight RA. Functional regulation of p73 and p63: development and cancer. Trends Biochem Sci 2003; 28: 663–70. - PubMed
-
- Yang A, Schweitzer R, Sun D et al p63 is essential for regenerative proliferation in limb, craniofacial and epithelial development. Nature 1999; 398: 714–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

