A de novo substructure generation algorithm for identifying the privileged chemical fragments of liver X receptorβ agonists
- PMID: 28894088
- PMCID: PMC5593923
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-08848-4
A de novo substructure generation algorithm for identifying the privileged chemical fragments of liver X receptorβ agonists
Abstract
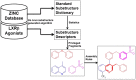
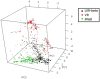
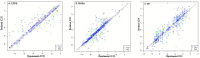
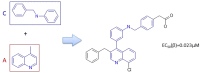
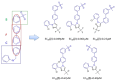
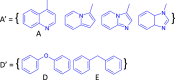
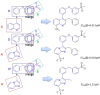
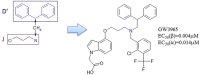
Liver X receptorβ (LXRβ) is a promising therapeutic target for lipid disorders, atherosclerosis, chronic inflammation, autoimmunity, cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. Druggable LXRβ agonists have been explored over the past decades. However, the pocket of LXRβ ligand-binding domain (LBD) is too large to predict LXRβ agonists with novel scaffolds based on either receptor or agonist structures. In this paper, we report a de novo algorithm which drives privileged LXRβ agonist fragments by starting with individual chemical bonds (de novo) from every molecule in a LXRβ agonist library, growing the bonds into substructures based on the agonist structures with isomorphic and homomorphic restrictions, and electing the privileged fragments from the substructures with a popularity threshold and background chemical and biological knowledge. Using these privileged fragments as queries, we were able to figure out the rules to reconstruct LXRβ agonist molecules from the fragments. The privileged fragments were validated by building regularized logistic regression (RLR) and supporting vector machine (SVM) models as descriptors to predict a LXRβ agonist activities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






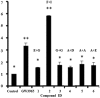
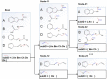
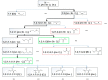
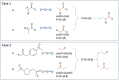
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

