Comparison of Cartesian and radial acquisition on short-tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequences in breast MRI
- PMID: 28894328
- PMCID: PMC5586511
- DOI: 10.1590/0100-3984.2015-0197
Comparison of Cartesian and radial acquisition on short-tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequences in breast MRI
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to compare two short-tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequences, Cartesian and radial (BLADE) acquisitions, for breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examinations.
Materials and methods: Ninety-six women underwent 1.5 T breast MRI exam (48 Cartesian and 48 BLADE). Qualitative analysis including image artifacts, image quality, fat-suppression, chest-wall depiction, lesion detection, lymph node depiction and overall impression were evaluated by three blinded readers. Signal to noise ratios (SNRs) were calculated. Cronbach's alpha test was used to assess inter-observer agreement. Subanalyses of image quality, chest-wall depiction and overall impression in 15 patients with implants and image quality in 31 patients with clips were correlated using Pearson test. Wilcoxon rank sum test and t-test were performed.
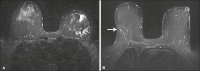
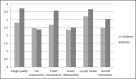
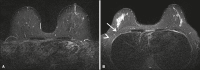
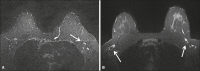
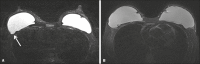
Results: Motion artifacts were present in 100% and in 0% of the Cartesian and the BLADE exams, respectively. Chemical-shift artifacts were present in 8% of the Cartesian exams. Flow artifacts were more frequent on BLADE. BLADE sequence was statistically superior to Cartesian for all qualitative features (p < 0.05) except for fat-suppression (p = 0.054). In the subanalysis, BLADE was superior for implants and clips (p < 0.05). SNR was statistically greater for BLADE (48.35 vs. 16.17). Cronbach ranged from 0.502 to 0.813.
Conclusion: BLADE appears to be superior to Cartesian acquisition of STIR imaging as measured by improved image quality, fewer artifacts, and improved chest wall and lymph node depiction.
Objetivo: Comparar duas sequências de aquisição, cartesiana e radial (BLADE) ponderadas em short-tau inversion recovery (STIR), em exames de ressonância magnética de mama.
Materiais e métodos: Noventa e seis pacientes foram submetidas a exame de ressonância magnética de mama em 1,5 T (48 aquisições STIR cartesianas e 48 aquisições STIR BLADE). A análise qualitativa incluindo artefatos, qualidade de imagem, supressão de gordura, avaliação da parede torácica, detecção de lesões, linfonodos e impressão geral foi avaliada independentemente por três leitores. Os signal to noise ratios (SNRs) foram calculados. Foi utilizado o teste alfa de Cronbach para avaliar a concordância interobservador. Subanálises da qualidade de imagem, avaliação da parede torácica e impressão geral em 15 pacientes com implantes e qualidade de imagem em 31 pacientes com clipes cirúrgicos foram correlacionadas aplicando o teste de Pearson. Os testes de Wilcoxon rank sum test e Student t foram utilizados para comparação qualitativa e quantitativa entre as duas sequências.
Resultados: Os artefatos de movimento estavam presentes em 100% e 0% dos exames de aquisição cartesiana e de BLADE, respectivamente. Os artefatos de desvio químico estavam presentes em 8% dos exames cartesianos. Artefatos de fluxo foram mais frequentes nas sequências BLADE. A sequência BLADE foi estatisticamente superior para todos os atributos qualitativos (p < 0,05), exceto na supressão de gordura (p = 0,054). O BLADE foi superior na avaliação dos implantes e clipes cirúrgicos (p < 0,05). O SNR foi estatisticamente superior na sequência BLADE (48,35 versus 16,17). Cronbach variou entre 0,502 e 0,813.
Conclusão: A sequência BLADE foi superior à sequência de aquisição cartesiana de imagens na ponderação STIR, comprovada por uma melhor qualidade de imagem, menos artefatos e melhor avaliação da parede torácica e de linfonodos.
Keywords: BLADE sequence; Breast MRI; Cartesian sequence; Image quality.
Figures
References
-
- Bassett LW, Dhaliwal SG, Eradat J, et al. National trends and practices in breast MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191:332–339. - PubMed
-
- Ballesio L, Savelli S, Angeletti M, et al. Breast MRI: are T2 IR sequences useful in the evaluation of breast lesions? Eur J Radiol. 2009;71:96–101. - PubMed
-
- Baltzer PA, Benndorf M, Dietzel M, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of unenhanced MR mammography (DWI combined with T2-weighted TSE imaging, ueMRM) for the differentiation of mass lesions. Eur Radiol. 2010;20:1101–1110. - PubMed
-
- Trimboli RM, Verardi N, Cartia F, et al. Breast cancer detection using double reading of unenhanced MRI including T1-weighted, T2-weighted STIR, and diffusion-weighted imaging: a proof of concept study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;203:674–681. - PubMed
-
- American College of Radiology CME for Journal Sept JACR14, Auditing a Breast MRI. [2015 May 10]. Internet. Available from: https://shop.acr.org/Default.aspx?TabID=55&ProductId=294382421.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
