FOXO Transcriptional Factors and Long-Term Living
- PMID: 28894507
- PMCID: PMC5574317
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/3494289
FOXO Transcriptional Factors and Long-Term Living
Abstract
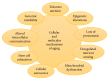
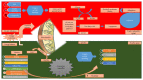
Several pathologies such as neurodegeneration and cancer are associated with aging, which is affected by many genetic and environmental factors. Healthy aging conceives human longevity, possibly due to carrying the defensive genes. For instance, FOXO (forkhead box O) genes determine human longevity. FOXO transcription factors are involved in the regulation of longevity phenomenon via insulin and insulin-like growth factor signaling. Only one FOXO gene (FOXO DAF-16) exists in invertebrates, while four FOXO genes, that is, FOXO1, FOXO3, FOXO4, and FOXO6 are found in mammals. These four transcription factors are involved in the multiple cellular pathways, which regulate growth, stress resistance, metabolism, cellular differentiation, and apoptosis in mammals. However, the accurate mode of longevity by FOXO factors is unclear until now. This article describes briefly the existing knowledge that is related to the role of FOXO factors in human longevity.
Figures
References
-
- Atzmon G., Schechter C., Greiner W., Davidson D., Rennert G., Barzilai N. Clinical phenotype of families with longevity. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2004;52:274–277. - PubMed
-
- Willcox B. J., Willcox D. C., He Q., Curb J. D., Suzuki M. Siblings of Okinawan centenarians share lifelong mortality advantages. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2006;61:345–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

