Anthropometric, physical function and general health markers of Masters athletes: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 28894644
- PMCID: PMC5592080
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.3768
Anthropometric, physical function and general health markers of Masters athletes: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
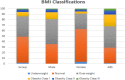
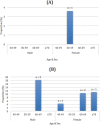
Once the general decline in muscle mass, muscle strength and physical performance falls below specific thresholds, the middle aged or older adult will be diagnosed as having sarcopenia (a loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength). Sarcopenia contributes to a range of adverse events in older age including disability, hospitalisation, institutionalisation and falls. One potentially relevant but understudied population for sarcopenia researchers would be Masters athletes. Masters sport is becoming more common as it allows athletes (typically 40 years and older) the opportunity to participate in individual and/or team sports against individuals of similar age. This study examined a variety of measures of anthropometric, physical function and general health markers in the male and female Masters athletes who competed at the 2014 Pan Pacific Masters Games held on the Gold Coast, Australia. Bioelectrical impedance analysis was used to collect body fat percentage, fat mass and fat-free mass; with body mass, height, body mass index (BMI) and sarcopenic status also recorded. Physical function was quantified by handgrip strength and habitual walking speed; with general health described by the number of chronic diseases and prescribed medications. Between group analyses utilised ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc tests to examine the effect of age group (40-49, 50-59, 60-69 and >70 years old) on the outcome measures for the entire sample as well as the male and female sub-groups. A total of 156 athletes (78 male, 78 female; mean 55.7 years) provided informed consent to participate in this study. These athletes possessed substantially better anthropometric, physical function and general health characteristics than the literature for their less physically active age-matched peers. No Masters athletes were categorised as being sarcopenic, although one participant had below normal physical performance and six participants had below normal muscle strength. In contrast, significant age-related reductions in handgrip strength and increases in the number of chronic diseases and prescribed medications were observed for the overall cohort as well as the male and female sub-groups. Nevertheless, even those aged over 70 years only averaged one chronic disease and one prescribed medication. These results may suggest that participation in Masters sport helps to maintain anthropometry, physical function and general health in middle-aged and older adults. However, it is also possible that only healthier middle-aged and older adults with favourable body composition and physical function may be able to participate in Masters sport. Future research should therefore utilise longitudinal research designs to determine the health and functional benefits of Master sports participation for middle-aged and older adults.
Keywords: Ageing; Anthropometric; General health; Masters athletes; Muscle mass; Muscle strength; Physical function; Physical performance; Sarcopenia; Sport.
Conflict of interest statement
Timothy Henwood is the Group Manager, Connected Living—Community Wellness and Lifestyle of Southern Cross Care (SA & NT) Inc., Adelaide, South Australia, Australia. Justin W.L. Keogh is an Academic Editor for PeerJ.
Figures
References
-
- Abellan van Kan G, Rolland Y, Andrieu S, Bauer J, Beauchet O, Bonnefoy M, Cesari M, Donini LM, Gillette Guyonnet S, Inzitari M, Nourhashemi F, Onder G, Ritz P, Salva A, Visser M, Vellas B. Gait speed at usual pace as a predictor of adverse outcomes in community-dwelling older people an International Academy on Nutrition and Aging (IANA) Task Force. Journal of Nutrition, Health and Aging. 2009;13:881–889. doi: 10.1007/s12603-009-0246-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Australian Bureau of Statistics Australian health survey: first results, 2011–12. 2012. http://www.abs.gov.au/AUSSTATS/abs@.nsf/DetailsPage/4364.0.55.0012011-12... http://www.abs.gov.au/AUSSTATS/abs@.nsf/DetailsPage/4364.0.55.0012011-12...
-
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare . Australia’s Health 2014. Australia’s health series no 14 Cat no AUS 178. Australian Institute of Health and Welfare; Canberra: 2014.
-
- Avery FD, Lyman OB, Congregational Church (Columbia Conn.: Town) The 150th anniversary of the organization of the Congregational Church in Columbia, Conn., October 24th, 1866: historical papers, addresses: with appendix. Hartford: Printed by Case, Lockwood & Co; 1867.
-
- Bai HJ, Sun JQ, Chen M, Xu DF, Xie H, Yu ZW, Bao ZJ, Chen J, Pan YR, Lu DJ, Cheng S. Age-related decline in skeletal muscle mass and function among elderly men and women in Shanghai, China: a cross sectional study. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2016;25:326–332. doi: 10.6133/apjcn.2016.25.2.14. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

