The Effectiveness of Electrical Acupuncture Stimulation in Reducing Levels of Self-reported Anxiety of Lung Cancer Patients during Palliative Care: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 28894706
- PMCID: PMC5575384
The Effectiveness of Electrical Acupuncture Stimulation in Reducing Levels of Self-reported Anxiety of Lung Cancer Patients during Palliative Care: A Pilot Study
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is a serious threat to human health and life worldwide. Anxiety is common amongst palliative care patients with lung cancer and adversely affects quality of life. Acupuncture is an effective and safe treatment method used for the treatment of depressive mood status. We aimed to assess the influence of electrical acupuncture stimulation on self-reported anxiety in palliative care among patients with lung cancer.
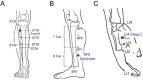
Methods: This pilot study had an experimental, 3-group, research plan. A total of 188 participants were enrolled from the Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, Tongji University, Shanghai, China from 2014-2015. This pilot study had an experimental, 3-group, research plan. In TEAS group, participants received standardized palliative care and electrical acupuncture stimulation in Zusanli, Sanyinjiao and Hegu acu-points. Group MS received standardized palliative care and muscle stimulation nearby nonacupoint. Controlled group received standardized palliative care. The patients maintained their assigned acupuncture stimulation for 7 days. Demographic Instrument, Karnofsky Performance Scale Index, SF-16 health questionnaire and Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) were used.
Results: The mean SAS scores in TEAS Group before and after electrical intervention in palliative care intervention were 31.17±7.55,34.58±13.98 and 27.86±6.73, (P=0.00) QoL score showed elevation from 57.13 in 8th day to 60.12 in 28th day, rising further to 5%. Comfort Score showed continuous elevation trend for 28 days.
Conclusion: Electric acupuncture stimulation could reduce the anxiety of patients, promote rehabilitation and increase the quality of life among patients with lung cancer in palliative care.
Keywords: Electrical acupuncture stimulation; Lung cancer; Palliative care; Patients; Self-reported anxiety.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. (2011). Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin, 61(2): 69–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
