SOCS1 is an inducible negative regulator of interferon λ (IFN-λ)-induced gene expression in vivo
- PMID: 28900038
- PMCID: PMC5663890
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.788877
SOCS1 is an inducible negative regulator of interferon λ (IFN-λ)-induced gene expression in vivo
Abstract
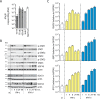
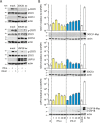
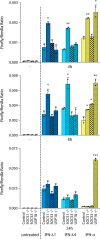
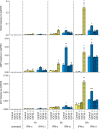
Type I (α and β) and type III (λ) IFNs are induced upon viral infection through host sensory pathways that activate IFN regulatory factors (IRFs) and nuclear factor κB. Secreted IFNs induce autocrine and paracrine signaling through the JAK-STAT pathway, leading to the transcriptional induction of hundreds of IFN-stimulated genes, among them sensory pathway components such as cGAS, STING, RIG-I, MDA5, and the transcription factor IRF7, which enhance the induction of IFN-αs and IFN-λs. This positive feedback loop enables a very rapid and strong host response that, at some point, has to be controlled by negative regulators to maintain tissue homeostasis. Type I IFN signaling is controlled by the inducible negative regulators suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1), SOCS3, and ubiquitin-specific peptidase 18 (USP18). The physiological role of these proteins in IFN-γ signaling has not been clarified. Here we used knockout cell lines and mice to show that IFN-λ signaling is regulated by SOCS1 but not by SOCS3 or USP18. These differences were the basis for the distinct kinetic properties of type I and III IFNs. We found that IFN-α signaling is transient and becomes refractory after hours, whereas IFN-λ provides a long-lasting IFN-stimulated gene induction.
Keywords: Hepatitis C virus (HCV); IFN λ; JAK; STAT transcription factor; interferon; suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3).
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

References
-
- Darnell J. E., Jr. (1997) STATs and gene regulation. Science 277, 1630–1635 - PubMed
-
- Krebs D. L., and Hilton D. J. (2001) SOCS proteins: negative regulators of cytokine signaling. Stem Cells 19, 378–387 - PubMed
-
- Dill M. T., Makowska Z., Trincucci G., Gruber A. J., Vogt J. E., Filipowicz M., Calabrese D., Krol I., Lau D. T., Terracciano L., van Nimwegen E., Roth V., and Heim M. H. (2014) Pegylated IFN-alpha regulates hepatic gene expression through transient Jak/STAT activation. J. Clin. Invest. 124, 1568–1581 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

