miR-618 Inhibits Prostate Cancer Migration and Invasion by Targeting FOXP2
- PMID: 28900488
- PMCID: PMC5595080
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.17407
miR-618 Inhibits Prostate Cancer Migration and Invasion by Targeting FOXP2
Abstract
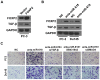
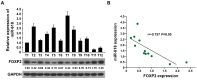
miRNAs play critical role in the development and progression of prostate cancer. Here we studied the role of miR-618 in prostate cancer migration and invasion. miR-618 was downregulated in metastatic androgen-independent prostate cancer (AIPC), patients with low miR-618 had poor outcome. Overexpression of miR-618 inhibited migration and invasion and induced mesenchymal to epithelial transition (MET). Conversely, knockdown of miR-618 promoted migration and invasion and induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT). FOXP2 was the direct target of miR-618, and promoted TGF-β expression, inhibition of TGF-β reversed the effect of miR-618 knockdown. We further analyzed the correlation between miR-618 expression and FOXP2 in human prostate cancer tissues, and found there was a negative correlation between miR-618 expression and FOXP2 levels. In conclusion, we found miR-618 inhibited prostate cancer migration and invasion by targeting FOXP2 and inhibiting TGF-β.
Keywords: FOXP2; TGF-β.; miR-618; migration; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
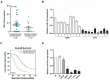
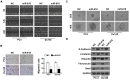
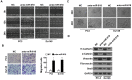
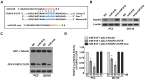
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-132/212 Upregulation Inhibits TGF-β-Mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Prostate Cancer Cells by Targeting SOX4.Prostate. 2016 Dec;76(16):1560-1570. doi: 10.1002/pros.23241. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Prostate. 2016. PMID: 27527117
-
Loss of miR-100 enhances migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness properties in prostate cancer cells through targeting Argonaute 2.Int J Oncol. 2014 Jul;45(1):362-72. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2413. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24805183
-
MiR-940 inhibits TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell invasion by targeting Snail in non-small cell lung cancer.J Cancer. 2019 Jun 2;10(12):2735-2744. doi: 10.7150/jca.31800. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31258781 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-145 and miR-203 represses TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion by inhibiting SMAD3 in non-small cell lung cancer cells.Lung Cancer. 2016 Jul;97:87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.04.017. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Lung Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27237033
-
The untold stories of the speech gene, the FOXP2 cancer gene.Genes Cancer. 2018 Jan;9(1-2):11-38. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.169. Genes Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29725501 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating miR-618 Has Prognostic Significance in Patients with Metastatic Colon Cancer.Curr Oncol. 2021 Mar 15;28(2):1204-1215. doi: 10.3390/curroncol28020116. Curr Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33804070 Free PMC article.
-
miR-205-5p inhibits cell migration and invasion in prostatic carcinoma by targeting ZEB1.Oncol Lett. 2018 Aug;16(2):1715-1721. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8862. Epub 2018 May 31. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30008858 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA circ-ATAD1 suppresses miR-618 maturation to participate in colorectal cancer.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 May 3;22(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02183-3. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35505304 Free PMC article.
-
miR-491-5p inhibits the proliferation and migration of A549 cells by FOXP4.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jun;21(6):622. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10054. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33936279 Free PMC article.
-
miR-618: possible control over TIMP-1 and its expression in localized prostate cancer.BMC Cancer. 2018 Oct 19;18(1):992. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4930-4. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30340564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradford TJ, Tomlins SA, Wang X, Chinnaiyan AM. Molecular markers of prostate cancer. Urologic oncology. 2006;24(6):538–551. - PubMed
-
- Varambally S, Dhanasekaran SM, Zhou M, Barrette TR, Kumar-Sinha C, Sanda MG, Ghosh D, Pienta KJ, Sewalt RG, Otte AP. et al. The polycomb group protein EZH2 is involved in progression of prostate cancer. Nature. 2002;419(6907):624–629. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

