A review of demodulation techniques for amplitude-modulation atomic force microscopy
- PMID: 28900596
- PMCID: PMC5530615
- DOI: 10.3762/bjnano.8.142
A review of demodulation techniques for amplitude-modulation atomic force microscopy
Abstract
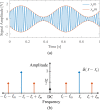
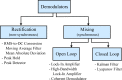
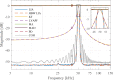
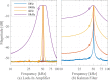
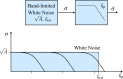
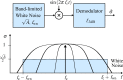
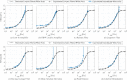
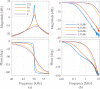
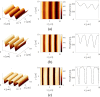
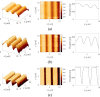
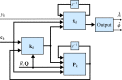
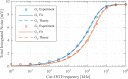
In this review paper, traditional and novel demodulation methods applicable to amplitude-modulation atomic force microscopy are implemented on a widely used digital processing system. As a crucial bandwidth-limiting component in the z-axis feedback loop of an atomic force microscope, the purpose of the demodulator is to obtain estimates of amplitude and phase of the cantilever deflection signal in the presence of sensor noise or additional distinct frequency components. Specifically for modern multifrequency techniques, where higher harmonic and/or higher eigenmode contributions are present in the oscillation signal, the fidelity of the estimates obtained from some demodulation techniques is not guaranteed. To enable a rigorous comparison, the performance metrics tracking bandwidth, implementation complexity and sensitivity to other frequency components are experimentally evaluated for each method. Finally, the significance of an adequate demodulator bandwidth is highlighted during high-speed tapping-mode atomic force microscopy experiments in constant-height mode.
Keywords: amplitude estimation; amplitude modulation; atomic force microscopy; digital signal processing; field-programmable gate array.
Figures
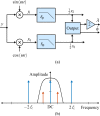
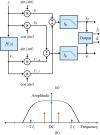
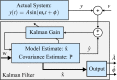
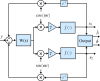
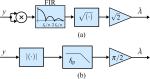
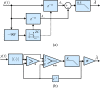
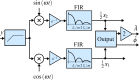
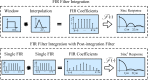
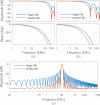
 , the frequency response of the interpolation filter can be neglected.
, the frequency response of the interpolation filter can be neglected.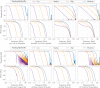

References
-
- Haykin S. Communication systems. John Wiley & Sons; 2008.
-
- Nyce D S. Linear position sensors: theory and application. John Wiley & Sons; 2004.
-
- Baxter L K. Capacitive sensors: Design and Applications. Wiley-IEEE Press; 1996.
-
- Fleming A J. Sens Actuators, A. 2013;190:106–126. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2012.10.016. - DOI
-
- Tsui D C, Stormer H L, Gossard A C. Phys Rev Lett. 1982;48:1559–1562. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.48.1559. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
