Effects of anticholinergic agent on miRNA profiles and transcriptomes in a murine model of allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 28901404
- PMCID: PMC5865825
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7411
Effects of anticholinergic agent on miRNA profiles and transcriptomes in a murine model of allergic rhinitis
Abstract
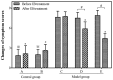
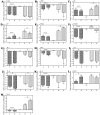
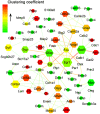
Anticholinergic agent, ipratropium bromide (IB) ameliorates symptoms of allergic rhinitis (AR) using neuroimmunologic mechanisms. However, the underlying molecular mechanism remains largely unclear. In the present study, 27 mice with AR induced by ovalbumin were randomly allocated to one of three groups: Model group, model group with IB treatment for 2 weeks, and model group with IB treatment for 4 weeks. Allergic symptoms were evaluated according to symptoms scores. Differentially expressed genes [microRNAs (miRNAs) and messenger RNAs (mRNAs)] of nasal mucosa were identified by microarray analysis. The expression levels of candidate genes were measured by reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT‑qPCR). The data indicates that the symptoms scores in allergic mice were significantly reduced by IB treatment. In the nasal mucosa of allergic mice with IB treatment, 207 mRNAs and 87 miRNAs were differentially expressed, when compared with the sham group. IB treatment significantly downregulated the expression levels of interleukin‑4Rα and prostaglandin D2 synthase, whereas the leukemia inhibitory factor, A20 and nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 1 expression levels were upregulated. Similarly, the expression levels of mmu‑miR‑124‑3p/5p, ‑133b‑5p, ‑133a‑3p/5p, ‑384‑3p, ‑181a‑5p, ‑378a‑5p and ‑3071‑5p were significantly increased. RT‑qPCR data further validated these mRNA and miRNA expression levels. Thus, IB treatment regulated expression of allergic immune‑associated mRNAs and miRNAs of the nasal mucosa in allergic mice, which may be associated with ameliorated nasal allergic symptoms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
miR-31 attenuates murine allergic rhinitis by suppressing interleukin-13-induced nasal epithelial inflammatory responses.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jan;23(1):42. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11680. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33179116 Free PMC article.
-
Changes of T-helper type 1/2 cell balance by anticholinergic treatment in allergic mice.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014 Mar;112(3):249-55. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2013.12.014. Epub 2014 Jan 10. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24428969
-
[The changes of microRNA in nasal mucosa after the specific immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis in mice].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Mar;29(5):457-61, 465. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26103670 Chinese.
-
Spotlight on microRNAs in allergy and asthma.Allergy. 2021 Jun;76(6):1661-1678. doi: 10.1111/all.14646. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Allergy. 2021. PMID: 33128813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in Allergic Disease.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016 Sep;16(9):67. doi: 10.1007/s11882-016-0648-z. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016. PMID: 27585977 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Exposure to Sulfur Dioxide Before Sensitization Decreased the Production of Specific IgE in HDM-Sensitized Allergic Rhinitis Mice.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Apr 18;15:2477-2490. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S352397. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35465447 Free PMC article.
-
Icariin restrains NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated Th2 immune responses and ameliorates atopic dermatitis through modulating a novel lncRNA MALAT1/miR-124-3p axis.Pharm Biol. 2023 Dec;61(1):1249-1259. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2023.2244004. Pharm Biol. 2023. PMID: 37602424 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of miR-4492 and IL-10 is involved in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Nov;18(5):3968-3976. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8022. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31611936 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for the treatment of allergic rhinitis: A systematic review protocol.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Dec;97(51):e13772. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013772. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30572530 Free PMC article.
-
Increased miR-124-3p alleviates type 2 inflammatory response in allergic rhinitis via IL-4Rα.Inflamm Res. 2022 Nov;71(10-11):1271-1282. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01614-x. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35922673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Teng Y, Zhang R, Liu C, Zhou L, Wang H, Zhuang W, Huang Y, Hong Z. miR-143 inhibits interleukin-13-induced inflammatory cytokine and mucus production in nasal epithelial cells from allergic rhinitis patients by targeting IL13Rα1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;457:58–64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.12.058. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

