Investigating simulation-based metrics for characterizing linear iterative reconstruction in digital breast tomosynthesis
- PMID: 28901614
- PMCID: PMC5604860
- DOI: 10.1002/mp.12445
Investigating simulation-based metrics for characterizing linear iterative reconstruction in digital breast tomosynthesis
Abstract
Purpose: Simulation-based image quality metrics are adapted and investigated for characterizing the parameter dependences of linear iterative image reconstruction for DBT.
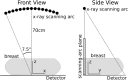
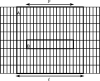
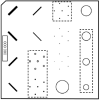
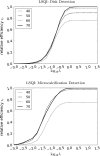
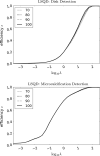
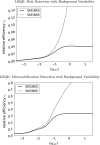
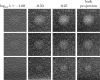
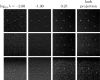
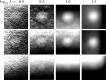
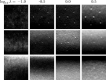
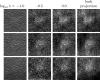
Methods: Three metrics based on a 2D DBT simulation are investigated: (1) a root-mean-square-error (RMSE) between the test phantom and reconstructed image, (2) a gradient RMSE where the comparison is made after taking a spatial gradient of both image and phantom, and (3) a region-of-interest (ROI) Hotelling observer (HO) for signal-known-exactly/background-known-exactly (SKE/BKE) and signal-known-exactly/background-known-statistically (SKE/BKS) detection tasks. Two simulation studies are performed using the aforementioned metrics, varying voxel aspect ratio, and regularization strength for two types of Tikhonov-regularized least-squares optimization. The RMSE metrics are applied to a 2D test phantom with resolution bar patterns at varying angles, and the ROI-HO metric is applied to two tasks relevant to DBT: lesion detection, modeled by use of a large, low-contrast signal, and microcalcification detection, modeled by use of a small, high-contrast signal. The RMSE metric trends are compared with visual assessment of the reconstructed bar-pattern phantom. The ROI-HO metric trends are compared with 3D reconstructed images from ACR phantom data acquired with a Hologic Selenia Dimensions DBT system.
Results: Sensitivity of the image RMSE to mean pixel value is found to limit its applicability to the assessment of DBT image reconstruction. The image gradient RMSE is insensitive to mean pixel value and appears to track better with subjective visualization of the reconstructed bar-pattern phantom. The ROI-HO metric shows an increasing trend with regularization strength for both forms of Tikhonov-regularized least-squares; however, this metric saturates at intermediate regularization strength indicating a point of diminishing returns for signal detection. Visualization with the reconstructed ACR phantom images appear to show a similar dependence with regularization strength.
Conclusions: From the limited studies presented it appears that image gradient RMSE trends correspond with visual assessment better than image RMSE for DBT image reconstruction. The ROI-HO metric for both detection tasks also appears to reflect visual trends in the ACR phantom reconstructions as a function of regularization strength. We point out, however, that the true utility of these metrics can only be assessed after amassing more data.
Keywords: Hotelling observer; digital breast tomosynthesis; image reconstruction; model observers; signal detection.
© 2017 American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures












References
-
- Wu T, Moore RH, Rafferty EA, Kopans DB. A comparison of reconstruction algorithms for breast tomosynthesis. Med Phys. 2004;31:2636–2647. - PubMed
-
- Sechopoulos I, Ghetti C. Optimization of the acquisition geometry in digital tomosynthesis of the breast. Med Phys. 2009;36:1199–1207. - PubMed
-
- Saunders RS, Samei E, Lo JY, Baker JA. Can compression be reduced for breast tomosynthesis? Monte carlo study on mass and microcalcification conspicuity in tomosynthesis. Radiology 2009;251:673–682. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

